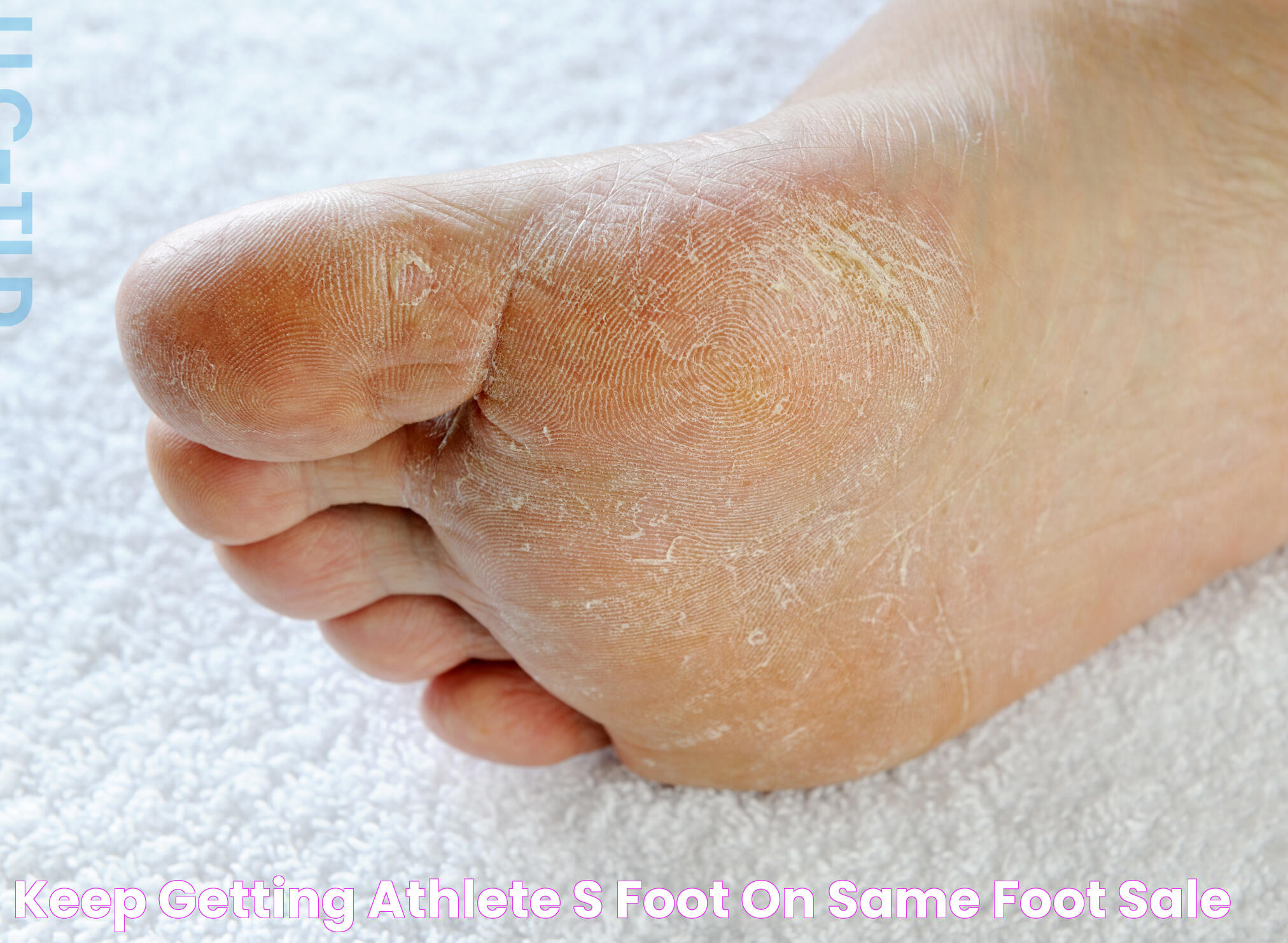
Athlete's foot, a common and often bothersome fungal infection, affects many people worldwide. This condition, medically known as tinea pedis, primarily targets the skin on the feet, causing itching, burning, and peeling. While the name suggests it only affects athletes, anyone exposed to the fungus can develop athlete's foot. Understanding how this infection occurs is crucial for effective prevention and treatment. In this article, we'll explore the causes, symptoms, and management strategies for athlete's foot, helping you protect your feet and maintain their health.
Many people wonder, "how do I get athlete's foot?" The answer lies in the environment and habits that foster the growth of fungi. Athlete's foot thrives in warm, moist environments such as communal showers, locker rooms, and swimming pools. It spreads through direct contact with surfaces contaminated by the fungus or through skin-to-skin contact with an infected person. Those with sweaty feet or a weakened immune system are more susceptible to contracting the infection. By recognizing these risk factors, individuals can take proactive steps to minimize their chances of developing athlete's foot.
Preventing athlete's foot involves maintaining good foot hygiene and adopting certain lifestyle changes. Regularly washing and thoroughly drying your feet, especially between the toes, can significantly reduce the risk of infection. Wearing breathable shoes and moisture-wicking socks also helps keep your feet dry and less hospitable to fungi. In this article, we'll delve deeper into the various preventative measures and explore effective treatments for those who may already be affected by athlete's foot. With the right knowledge and tools, you can keep your feet healthy and free from this common fungal infection.
Read also:Profound Teachings Scriptures On Mercy
Table of Contents
- What is Athlete's Foot?
- Symptoms of Athlete's Foot
- How Do I Get Athlete's Foot?
- Risk Factors
- Diagnosis
- Prevention Strategies
- Treatment Options
- When to See a Doctor?
- Home Remedies
- Complications
- Can Athlete's Foot Be Cured?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
- External Resources
What is Athlete's Foot?
Athlete's foot is a contagious fungal infection that affects the skin on the feet. It is caused by dermatophytes, a group of fungi that thrive in warm and moist environments. The infection typically starts between the toes and can spread to the sole, sides of the foot, and even the toenails if left untreated. Though common among athletes who frequent locker rooms and communal showers, athlete's foot can affect anyone, regardless of their athletic involvement.
Symptoms of Athlete's Foot
The symptoms of athlete's foot can vary depending on the severity of the infection. Common signs include:
- Itching and burning sensations between the toes or on the soles of the feet
- Red, scaly, or cracked skin
- Blisters or peeling skin
- Thickened or discolored toenails
- Unpleasant foot odor
If you experience any of these symptoms, it's important to seek treatment promptly to prevent the infection from worsening or spreading to other areas of the body.
How Do I Get Athlete's Foot?
Athlete's foot is primarily contracted through contact with fungal spores present on contaminated surfaces or through direct contact with an infected person. The fungi thrive in warm, damp environments, making places like public showers, locker rooms, and swimming pools common hotspots for transmission. Here are some ways you might get athlete's foot:
- Walking barefoot in communal areas
- Sharing towels, shoes, or socks with an infected individual
- Having damp or sweaty feet for extended periods
Understanding these transmission methods can help you take steps to protect yourself and reduce the risk of infection.
Risk Factors
Certain factors can increase the likelihood of developing athlete's foot. These include:
Read also:Sam Reid The Rising Star Illuminating Our Screens
- Frequenting communal showers, locker rooms, or swimming pools
- Having sweaty feet or wearing tight-fitting, non-breathable shoes
- Experiencing a weakened immune system
- Having a history of fungal infections
By recognizing and addressing these risk factors, individuals can better protect themselves from contracting athlete's foot.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing athlete's foot typically involves a physical examination of the affected area by a healthcare professional. In some cases, they may take skin scrapings for further analysis to confirm the presence of fungi. If the infection is severe or not responding to over-the-counter treatments, additional tests may be necessary to determine the best course of action.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing athlete's foot involves a combination of good hygiene practices and lifestyle changes. Some effective strategies include:
- Regularly washing and thoroughly drying your feet, especially between the toes
- Wearing moisture-wicking socks and breathable shoes
- Using antifungal powders or sprays in shoes and on feet
- Avoiding walking barefoot in communal areas
- Not sharing towels, shoes, or socks with others
Implementing these preventative measures can significantly reduce your risk of developing athlete's foot.
Treatment Options
Treating athlete's foot typically involves the use of antifungal medications, which can be purchased over-the-counter or prescribed by a healthcare professional. Common treatments include:
- Topical antifungal creams, ointments, or sprays
- Oral antifungal medications for severe or persistent cases
- Home remedies such as tea tree oil or vinegar soaks
It's important to follow the instructions provided with these treatments and continue using them for the recommended duration to ensure the infection is fully eradicated.
When to See a Doctor?
While many cases of athlete's foot can be treated with over-the-counter medications, it's important to consult a healthcare professional if:
- The infection doesn't improve within two weeks
- You have a weakened immune system or diabetes
- The infection spreads to other parts of the body
- You're experiencing severe pain, swelling, or redness
A doctor can provide a more comprehensive treatment plan and ensure the infection is properly managed.
Home Remedies
In addition to conventional treatments, several home remedies may help alleviate symptoms and promote healing. These include:
- Soaking feet in a mixture of water and vinegar
- Applying tea tree oil to the affected area
- Using garlic paste as a natural antifungal
While these remedies can be effective, it's important to use them in conjunction with medical treatments to achieve the best results.
Complications
If left untreated, athlete's foot can lead to several complications, including:
- Spread of the infection to other parts of the body, such as the toenails or hands
- Secondary bacterial infections
- Chronic or recurring infections
Prompt treatment and proper foot care can help prevent these complications and ensure a quicker recovery.
Can Athlete's Foot Be Cured?
Yes, with proper treatment and care, athlete's foot can be effectively cured. Antifungal medications, combined with good foot hygiene and preventative measures, can eliminate the infection and reduce the risk of recurrence. However, it's important to continue treatment as directed and maintain preventive practices to keep the infection at bay.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main causes of athlete's foot?
Athlete's foot is primarily caused by exposure to dermatophytes, a group of fungi that thrive in warm, moist environments. Common sources include communal showers, locker rooms, and swimming pools.
Can athlete's foot spread to other parts of the body?
Yes, if left untreated, athlete's foot can spread to other areas, such as the toenails, hands, and even the groin area. Prompt treatment is essential to prevent this spread.
Is athlete's foot contagious?
Yes, athlete's foot is highly contagious and can spread through direct contact with an infected person or contaminated surfaces.
How long does it take to treat athlete's foot?
The duration of treatment depends on the severity of the infection. Mild cases may resolve within a few weeks with over-the-counter medications, while more severe cases may require longer treatment.
Can I prevent athlete's foot from recurring?
Yes, maintaining good foot hygiene, wearing breathable footwear, and avoiding communal areas barefoot can help prevent recurrence.
Are home remedies effective for treating athlete's foot?
While home remedies can help alleviate symptoms, they should be used alongside medical treatments for the best results.
Conclusion
Athlete's foot, though common and contagious, can be effectively managed with the right knowledge and treatment. Understanding how the infection occurs, recognizing the symptoms, and implementing preventive measures are key to keeping your feet healthy and free from this bothersome condition. By following the comprehensive strategies outlined in this article, you can reduce your risk of contracting athlete's foot and ensure a swift recovery if you do become infected.
External Resources
For more detailed information on athlete's foot and its treatment, you can visit the Mayo Clinic's website on Athlete's Foot.