The concept of ego has intrigued psychologists, philosophers, and thinkers for centuries, leading to a myriad of interpretations and understandings. At its core, ego is often perceived as the part of the human psyche that manages one's sense of identity and self-worth. It's a critical component of our consciousness, influencing how we perceive ourselves and interact with the world around us. With its roots deeply embedded in both psychological and philosophical discourse, the ego serves as a mediator between our inner desires and external realities.
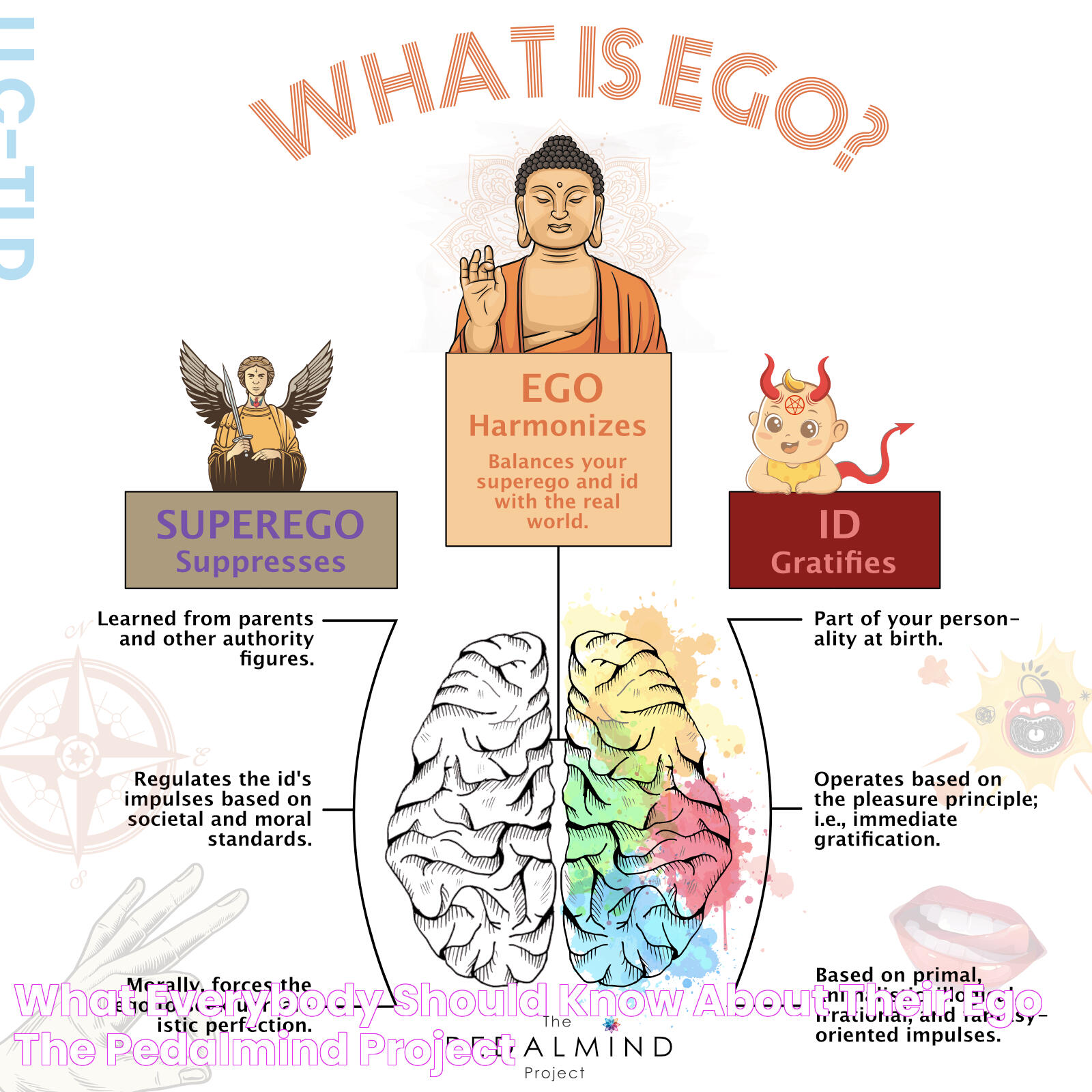
In psychological terms, the ego is a central element of Sigmund Freud's structural model of the psyche, which includes the id, ego, and superego. The ego is responsible for mediating the demands of the id (instinctual desires) and the superego (moral standards) while maintaining a realistic sense of self within the confines of reality. This balancing act is crucial for healthy psychological functioning, as it allows individuals to navigate their desires, ethics, and rationality effectively. The ego is thus seen as a stabilizing force, essential for maintaining a coherent and adaptable personality.
Philosophically, the ego is often associated with the self or the "I" that experiences and reflects upon the world. It raises profound questions about identity, consciousness, and the nature of self-awareness. Some philosophical traditions, notably in Eastern thought, challenge the conventional understanding of ego by advocating for the dissolution of ego-driven desires and promoting a more holistic integration with the universe. This duality in understanding highlights the complexity and multifaceted nature of the ego, necessitating a comprehensive exploration to fully grasp its significance in both personal and universal contexts.
Read also:Mastering The Art Of Gun Clan Tag In Cod A Guide To Success
Table of Contents
- What is the Ego?
- Historical Perspectives on Ego
- Freudian Concepts
- Philosophical Views of Ego
- Ego in Modern Psychology
- How Does Ego Influence Our Behavior?
- Ego and Self-Esteem
- Ego vs. True Self
- Can Ego Be Beneficial?
- The Dark Side of Ego
- Overcoming Ego-Driven Behavior
- Ego in Popular Culture
- Influence of Ego in Relationships
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What is the Ego?
The ego is a multifaceted concept that plays a crucial role in our understanding of self and the world. It is often defined as the part of the mind that mediates between the conscious and the subconscious, balancing desires, and moral values. In simple terms, the ego is the self or "I" that perceives, makes decisions, and interacts with the environment.
In psychological terms, particularly within Freudian theory, the ego is one of the three components of the psyche. It is responsible for reality testing and a sense of personal identity. The ego operates on the reality principle, negotiating between the id, which represents innate biological drives, and the superego, which embodies internalized societal norms and ethics.
Philosophically, the ego is often linked to self-awareness and identity. It is the centric 'I' that thinks, perceives, and experiences life. This perspective raises deep questions about the nature of consciousness and the true self, inviting debates about whether the ego is an illusion or an intrinsic part of being human.
Historical Perspectives on Ego
The concept of ego has evolved significantly over time, influenced by various cultural and intellectual traditions. In ancient philosophy, the ego was often intertwined with notions of the soul and self-awareness. Greek philosophers such as Socrates and Plato pondered the nature of the self, with Plato's "Allegory of the Cave" symbolizing the journey from ignorance to enlightenment—a journey often mediated by the ego.
During the Enlightenment, the ego took on new dimensions as thinkers like Descartes emphasized rational thought and self-awareness. Descartes' famous dictum "Cogito, ergo sum" ("I think, therefore I am") underscores the centrality of the ego in establishing existence and consciousness.
In the modern era, the work of Sigmund Freud revolutionized the understanding of the ego within psychological discourse. Freud's model of the psyche, comprising the id, ego, and superego, has profoundly influenced both psychological theory and cultural perceptions of selfhood.
Read also:All About Nikkita Lyons A Rising Star In The World Of Wrestling
Freudian Concepts
Sigmund Freud's theories on the ego are foundational to psychoanalytic thought. Freud posited that the human psyche is structured into three parts: the id, ego, and superego. The id is the primal, instinctual component seeking immediate gratification, while the superego represents internalized cultural norms and ideals.
The ego, according to Freud, serves as the rational mediator between the often-conflicting demands of the id and the superego. It operates based on the reality principle, navigating the external world to satisfy the id's desires in socially acceptable ways. This balancing act is crucial for maintaining psychological equilibrium.
Freud's concept of the ego defense mechanisms highlights how the ego protects itself from anxiety and conflict. These mechanisms, such as repression, denial, and projection, are strategies the ego employs to manage internal tensions and external pressures.
Philosophical Views of Ego
Beyond psychology, the ego has been a subject of intense philosophical scrutiny. In Western philosophy, the ego is often associated with individual identity and consciousness. Philosophers like Immanuel Kant and Friedrich Nietzsche explored the ego's role in shaping human perception and morality.
In contrast, Eastern philosophies like Buddhism and Taoism offer a different perspective. They often view the ego as an illusion or barrier to true enlightenment. These traditions emphasize transcending the ego to achieve a more interconnected and harmonious existence.
Ego in Modern Psychology
Modern psychology continues to explore and expand upon Freud's foundational ideas about the ego. Contemporary theorists have developed various models and frameworks to understand the ego's role in mental health and personal development.
One such approach is Carl Jung's concept of the "persona" and "shadow," which examines the ego's role in presenting different aspects of self to the world. Jung emphasized the importance of integrating these facets to achieve individuation and self-actualization.
Additionally, modern therapy practices, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), focus on the ego's role in shaping thought patterns and behaviors. By understanding and modifying the ego's influence, individuals can address cognitive distortions and improve emotional well-being.
How Does Ego Influence Our Behavior?
The ego plays a pivotal role in shaping our behaviors and interactions with the world. It influences our decision-making processes, self-perception, and how we respond to challenges and opportunities.
At its core, the ego seeks to protect our self-image and maintain a sense of coherence and stability. This can lead to behaviors aimed at preserving self-esteem and avoiding situations that threaten our identity. However, an overly dominant ego can result in narcissism, defensiveness, and an inability to accept criticism.
Understanding the ego's influence on behavior is crucial for personal growth and development. By recognizing when the ego is driving actions and reactions, individuals can make more conscious and deliberate choices, leading to healthier relationships and greater self-awareness.
Ego and Self-Esteem
The relationship between ego and self-esteem is complex and multifaceted. Self-esteem refers to an individual's overall sense of self-worth and value, while the ego is the mechanism through which this self-perception is maintained and protected.
A healthy ego contributes to balanced self-esteem, enabling individuals to acknowledge their strengths and weaknesses without undue self-criticism or arrogance. However, an inflated ego can lead to exaggerated self-esteem, resulting in narcissistic tendencies and an inability to empathize with others.
Conversely, an underdeveloped ego may contribute to low self-esteem, marked by self-doubt and insecurity. Building a healthy ego involves cultivating self-awareness, self-acceptance, and resilience, allowing for a more grounded and realistic self-esteem.
Ego vs. True Self
The distinction between the ego and the true self is a prevalent theme in both psychological and spiritual discourse. The ego is often seen as the constructed self, shaped by external influences and societal expectations, while the true self represents the authentic, unconditioned essence of an individual.
Many therapeutic and spiritual practices aim to help individuals transcend the ego to connect with their true self. This process involves self-reflection, introspection, and a willingness to let go of ego-driven desires and fears.
By aligning with the true self, individuals can experience greater authenticity, fulfillment, and inner peace. This journey requires ongoing self-awareness and a commitment to personal growth and transformation.
Can Ego Be Beneficial?
While the ego often receives a negative connotation, it can also play a beneficial role in personal development and achievement. A well-balanced ego provides the confidence and motivation needed to pursue goals and overcome obstacles.
The ego can drive ambition, creativity, and resilience, enabling individuals to assert themselves and navigate complex social dynamics. It is also essential for setting boundaries and advocating for one's needs in relationships and professional environments.
However, the key to harnessing the ego's positive aspects lies in maintaining balance and self-awareness. A healthy ego supports growth and empowerment without overshadowing empathy, humility, and connection with others.
The Dark Side of Ego
Despite its potential benefits, the ego can also manifest in destructive ways when left unchecked. An overinflated ego can lead to narcissism, entitlement, and a lack of empathy, damaging relationships and hindering personal growth.
The ego's need for validation and control can result in defensive behaviors, resistance to change, and an inability to accept criticism. This can create barriers to authentic communication and connection with others.
Recognizing and addressing the dark side of the ego is essential for personal development. By cultivating self-awareness and humility, individuals can mitigate the negative impacts of the ego and foster healthier relationships and a more fulfilling life.
Overcoming Ego-Driven Behavior
Overcoming ego-driven behavior involves a commitment to self-reflection, mindfulness, and personal growth. It requires recognizing when the ego is influencing actions and decisions and taking steps to align with one's true self.
Practices such as meditation, journaling, and therapy can help individuals gain insight into their ego-driven patterns and develop greater self-awareness. These practices encourage introspection and foster a deeper understanding of one's motivations and desires.
By cultivating self-compassion and embracing vulnerability, individuals can transcend ego-driven behaviors and cultivate more authentic and meaningful connections with themselves and others.
Ego in Popular Culture
The ego is a recurring theme in popular culture, often depicted in literature, film, and music. It is frequently explored as a source of conflict, character development, and narrative tension.
In literature, characters often undergo journeys of self-discovery that involve confronting and overcoming their egos. Similarly, films and television series frequently explore the complexities of ego-driven motivations and their impact on relationships and personal growth.
Music also reflects the theme of ego, with artists expressing their struggles and triumphs in navigating ego-driven desires and aspirations. These cultural representations highlight the universal and multifaceted nature of the ego in shaping human experience.
Influence of Ego in Relationships
The ego plays a significant role in shaping interpersonal dynamics and relationships. It can influence communication, conflict resolution, and the ability to empathize and connect with others.
An overactive ego can lead to power struggles, defensiveness, and an inability to see situations from another's perspective. This can create barriers to intimacy and mutual understanding in relationships.
Conversely, a healthy ego supports open communication, empathy, and collaboration. By recognizing and managing ego-driven behaviors, individuals can foster more harmonious and fulfilling relationships.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the main function of the ego?
- How does ego differ from self-esteem?
- Can the ego be eliminated?
- What are ego defense mechanisms?
- Is the ego always negative?
- How can I manage my ego?
The main function of the ego is to mediate between the unconscious desires of the id and the moral constraints of the superego, while navigating the realities of the external world to maintain a coherent sense of self.
While ego refers to the part of the psyche that manages identity and self-perception, self-esteem pertains to one's overall sense of self-worth. A healthy ego supports balanced self-esteem, but an inflated or underdeveloped ego can distort self-esteem.
In many spiritual traditions, the goal is not to eliminate the ego entirely but to transcend its limitations and integrate it with a deeper sense of self-awareness and connection with the universe.
Ego defense mechanisms are unconscious strategies the ego employs to protect itself from anxiety and conflict, such as repression, denial, and projection. These mechanisms help manage internal tensions and external pressures.
No, the ego is not inherently negative. It plays a vital role in personal development, self-confidence, and boundary-setting. However, unchecked ego can lead to narcissism and hinder authentic connections with others.
Managing the ego involves cultivating self-awareness, practicing mindfulness, and engaging in self-reflection. These practices help recognize ego-driven behaviors and align with one's true self for personal growth and fulfillment.
Conclusion
The ego is a multifaceted construct that plays a significant role in shaping identity, behavior, and relationships. It serves as a mediator between internal desires and external realities, influencing self-perception and interactions with the world.
Understanding the complexities of the ego is essential for personal growth and development. By recognizing its influence and cultivating self-awareness, individuals can navigate ego-driven behaviors and align with their true selves.
Ultimately, the ego is neither wholly beneficial nor detrimental; it is a vital component of the human experience that requires balance and mindfulness to harness its potential for personal and relational fulfillment.