The Myers Briggs Chart is an instrumental tool in decoding the complexities of personality types, often acting as a guide to understanding oneself and others. Developed from Carl Jung's theories by Katharine Cook Briggs and her daughter Isabel Briggs Myers, this psychological framework has become a cornerstone in personality assessment. It categorizes individuals into 16 distinct personality types based on preferences in four dichotomies: Introversion/Extraversion, Sensing/Intuition, Thinking/Feeling, and Judging/Perceiving.
In today's fast-paced world, the Myers Briggs Chart is not just a test but a journey into the depths of human personality. It provides insights into how individuals perceive the world and make decisions, fostering a better understanding of one's strengths and areas for growth. For many, it serves as a roadmap for personal development, career guidance, and improving interpersonal relationships.
While the Myers Briggs Chart has its critics, the popularity of this assessment continues to grow. Its applications range from corporate settings to educational institutions, and even in personal life. By understanding the nuances of each personality type, individuals can tailor their interactions and communication styles to better connect with others. Whether you're an individual seeking self-discovery or a professional aiming to enhance team dynamics, the Myers Briggs Chart offers valuable insights into the diverse spectrum of human personality.
Read also:English To Yoruba The Ultimate Language Translation Guide
Table of Contents
- History and Origins of the Myers Briggs Chart
- Understanding the Four Dichotomies
- The 16 Personality Types
- How is the Myers Briggs Chart Used Today?
- Benefits of the Myers Briggs Assessment
- Criticisms and Controversies
- The Role of Myers Briggs in Career Development
- Can the Myers Briggs Chart Improve Relationships?
- Myers Briggs and Team Dynamics
- How to Take the Myers Briggs Assessment
- Interpreting Your Myers Briggs Results
- Alternatives to the Myers Briggs Chart
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
History and Origins of the Myers Briggs Chart
The Myers Briggs Chart has a rich history that dates back to the early 20th century. It was inspired by Carl Jung’s theory of psychological types, which proposed that people experience the world through four principal psychological functions: sensation, intuition, feeling, and thinking. Jung's work laid the foundation for the development of the Myers Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI).
Katharine Cook Briggs and her daughter Isabel Briggs Myers were instrumental in translating Jung's complex theories into a practical tool that could be used to help people understand themselves and others better. Their goal was to make the theory of psychological types understandable and useful in people's lives. The first version of the MBTI was developed during World War II, initially helping women entering the workforce to identify the most suitable job roles based on their personality types.
Over the years, the Myers Briggs Chart has evolved, with numerous revisions and updates to enhance its accuracy and applicability. Today, it is one of the most widely used personality assessments in the world, with millions of people taking the test annually.
Understanding the Four Dichotomies
The Myers Briggs Chart categorizes personality types based on four dichotomies, each representing a spectrum between two opposing preferences. Understanding these dichotomies is key to grasping the essence of the MBTI.
Introversion vs. Extraversion
This dichotomy focuses on where individuals get their energy from. Introverts tend to recharge by spending time alone, focusing inward, and reflecting on thoughts and ideas. Extraverts, on the other hand, draw energy from social interactions and external activities.
Sensing vs. Intuition
Sensing and Intuition describe how people gather information from the world around them. Sensing types rely on concrete, factual information and prefer practical, hands-on experiences. Intuitive types look for patterns and possibilities, often relying on their instincts and imagination.
Read also:Yoruba To English Bridging Cultures Through Language
Thinking vs. Feeling
This dichotomy pertains to how individuals make decisions. Thinking types prioritize logic and objective criteria, often making decisions based on rational analysis. Feeling types consider emotions and values, aiming for harmony and consensus in their decision-making process.
Judging vs. Perceiving
Judging and Perceiving reflect how individuals approach the external world. Judging types prefer structure and order, planning their activities in advance. Perceiving types are more flexible and adaptable, preferring to keep their options open and go with the flow.
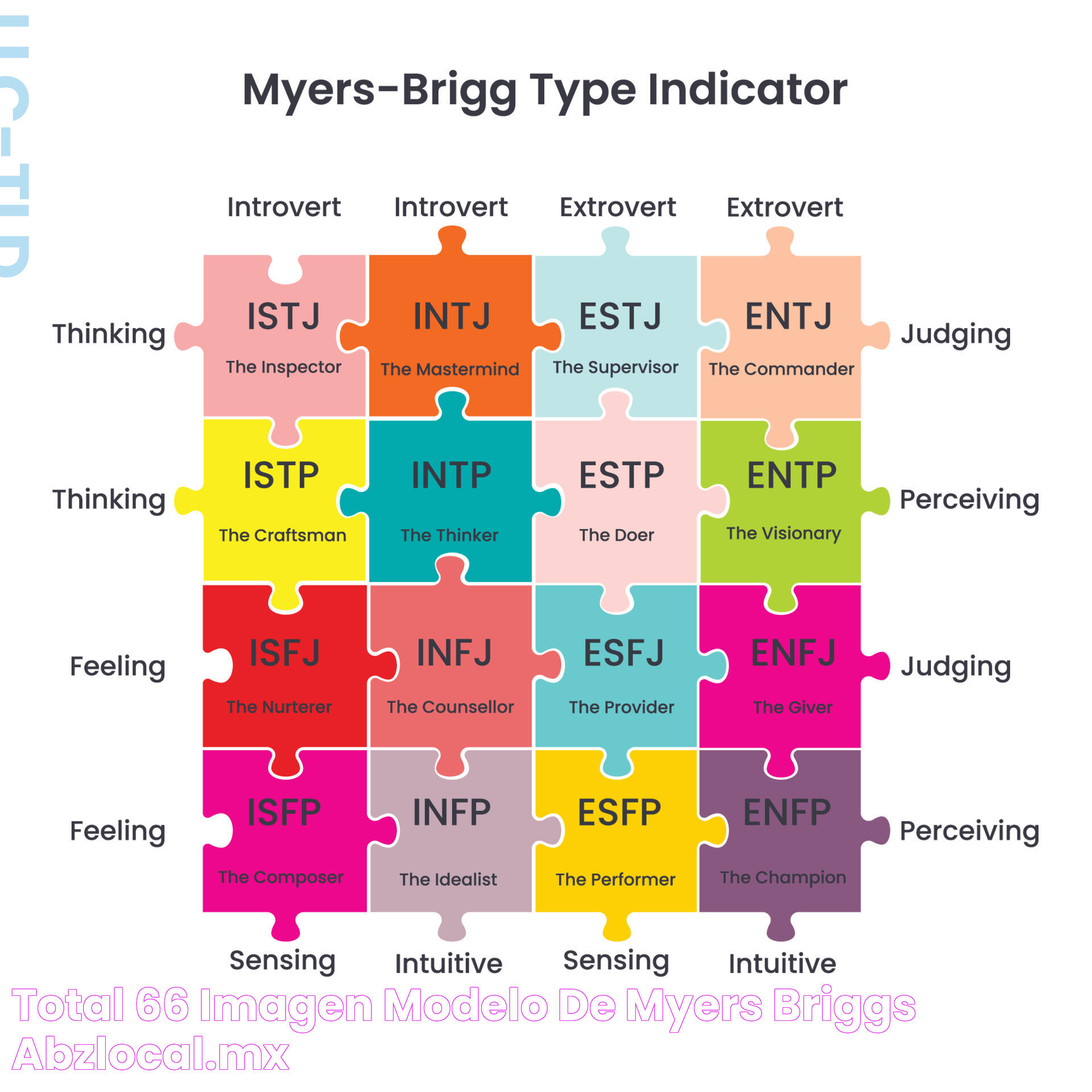
The 16 Personality Types
The Myers Briggs Chart categorizes individuals into 16 distinct personality types, each represented by a four-letter code. These types are derived from the combinations of the four dichotomies. Understanding these types can provide valuable insights into an individual's natural preferences and tendencies.
Below is a brief overview of each personality type:
- ISTJ (The Inspector): Responsible, detail-oriented, and dependable. Prefers structure and organization.
- ISFJ (The Protector): Warm, caring, and supportive. Values traditions and loyalty.
- INFJ (The Counselor): Insightful, idealistic, and empathetic. Driven by a deep sense of purpose.
- INTJ (The Mastermind): Strategic, independent, and analytical. Enjoys solving complex problems.
- ISTP (The Craftsman): Practical, adventurous, and resourceful. Prefers hands-on learning.
- ISFP (The Composer): Artistic, sensitive, and spontaneous. Values freedom and creativity.
- INFP (The Healer): Compassionate, introspective, and imaginative. Guided by personal values.
- INTP (The Architect): Curious, logical, and innovative. Enjoys exploring theoretical concepts.
- ESTP (The Dynamo): Energetic, spontaneous, and outgoing. Thrives in fast-paced environments.
- ESFP (The Performer): Charismatic, sociable, and adaptable. Enjoys entertaining and engaging with others.
- ENFP (The Champion): Enthusiastic, creative, and optimistic. Motivated by possibilities.
- ENTP (The Visionary): Innovative, curious, and witty. Enjoys debating and challenging ideas.
- ESTJ (The Supervisor): Organized, practical, and logical. Prefers clear guidelines and rules.
- ESFJ (The Provider): Caring, sociable, and cooperative. Values harmony and community.
- ENFJ (The Teacher): Charismatic, empathetic, and inspirational. Driven by a desire to help others grow.
- ENTJ (The Commander): Confident, strategic, and assertive. Natural leaders who enjoy taking charge.
How is the Myers Briggs Chart Used Today?
The Myers Briggs Chart has found applications in various fields, from personal development to professional growth. Its versatility makes it a valuable tool for understanding human behavior and enhancing communication.
In the workplace, the MBTI is often used for team building, leadership development, and conflict resolution. By understanding the diverse personality types within a team, organizations can foster a more inclusive and harmonious work environment. Managers can tailor their leadership styles to suit the preferences of their team members, leading to improved job satisfaction and productivity.
In educational settings, the Myers Briggs Chart helps students gain insights into their learning styles, enabling them to adopt study methods that align with their natural preferences. Educators can use the MBTI to create personalized learning experiences that cater to the diverse needs of their students.
On a personal level, the Myers Briggs Chart aids individuals in understanding their strengths and weaknesses, leading to increased self-awareness and personal growth. It can also improve interpersonal relationships by helping individuals appreciate and embrace the differences in others.
Benefits of the Myers Briggs Assessment
The Myers Briggs Assessment offers numerous benefits that contribute to its popularity and widespread use. Here are some of the key advantages:
- Self-Understanding: The MBTI provides individuals with a deeper understanding of their personality traits, helping them identify their strengths, weaknesses, and preferences.
- Improved Communication: By understanding the personality types of others, individuals can tailor their communication styles to build rapport and foster effective interactions.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: The MBTI helps individuals recognize their decision-making processes, enabling them to make more informed and balanced choices.
- Career Development: The assessment provides valuable insights into suitable career paths and work environments that align with one's personality.
- Conflict Resolution: Understanding different personality types can facilitate conflict resolution by promoting empathy and understanding.
Criticisms and Controversies
Despite its widespread use, the Myers Briggs Chart has faced criticism and controversy over the years. Critics argue that the MBTI lacks scientific validity and reliability, raising questions about its accuracy in assessing personality types.
One of the main criticisms is that the MBTI oversimplifies complex human behavior by categorizing individuals into fixed personality types. Critics also point out that the dichotomies are not mutually exclusive, as people may exhibit traits from both ends of the spectrum.
Furthermore, some researchers argue that the MBTI is not a predictive tool, meaning it may not accurately forecast behavior or performance in various contexts. Despite these criticisms, many proponents of the MBTI emphasize its value as a tool for self-reflection and personal development rather than a definitive measure of personality.
The Role of Myers Briggs in Career Development
The Myers Briggs Chart plays a significant role in career development by providing insights into an individual's natural preferences and work styles. Understanding one's personality type can guide individuals in choosing careers that align with their strengths and values.
For instance, introverted types may thrive in careers that allow for independent work and reflection, while extraverted types may excel in roles that involve teamwork and social interactions. Sensing types may prefer hands-on, practical work, while intuitive types may be drawn to creative and visionary roles.
Moreover, the MBTI can help individuals navigate career transitions by identifying transferable skills and areas for growth. It can also aid in setting career goals and developing strategies to achieve them.
Can the Myers Briggs Chart Improve Relationships?
Yes, the Myers Briggs Chart can improve relationships by promoting understanding and appreciation of individual differences. By recognizing the diverse personality types, individuals can tailor their communication and interaction styles to strengthen their relationships with others.
Understanding one's own personality type and the types of loved ones can lead to more empathetic and harmonious relationships. For example, recognizing the decision-making style of a partner can help avoid misunderstandings and conflicts, leading to more effective communication.
Moreover, the MBTI can enhance relationships by fostering open and honest discussions about preferences, needs, and expectations. This understanding can lead to stronger connections, improved collaboration, and mutual respect.
Myers Briggs and Team Dynamics
The Myers Briggs Chart is a valuable tool for understanding team dynamics and enhancing collaboration. By identifying the personality types within a team, leaders can create a balanced and cohesive group that leverages the strengths of each member.
For instance, teams with a mix of introverted and extraverted members can benefit from diverse perspectives and approaches to problem-solving. Sensing and intuitive types can complement each other by providing practical and visionary insights, respectively.
Moreover, understanding the MBTI can help teams address potential conflicts and communication barriers. By appreciating and valuing the differences in personality types, teams can work more effectively and achieve their goals.
How to Take the Myers Briggs Assessment
Taking the Myers Briggs Assessment is a straightforward process that involves completing a questionnaire designed to identify your personality type. The assessment can be taken online or through a certified MBTI practitioner.
The questionnaire consists of a series of questions that assess your preferences in the four dichotomies: Introversion/Extraversion, Sensing/Intuition, Thinking/Feeling, and Judging/Perceiving. Once completed, your responses are analyzed to determine your personality type, represented by a four-letter code.
It's important to approach the assessment with an open mind and answer the questions honestly. The accuracy of the results depends on your self-awareness and willingness to reflect on your true preferences.
Interpreting Your Myers Briggs Results
Interpreting your Myers Briggs results involves understanding the meaning behind your four-letter personality type code. Each letter represents a specific preference in the four dichotomies, providing insights into your natural tendencies and behaviors.
For example, an ISTJ (Introverted, Sensing, Thinking, Judging) personality type may indicate a preference for structure, logic, and practicality. In contrast, an ENFP (Extraverted, Intuitive, Feeling, Perceiving) type may suggest a preference for creativity, empathy, and adaptability.
While the MBTI provides valuable insights, it's important to remember that personality is complex and multifaceted. The assessment is a tool for self-reflection and growth, rather than a definitive label.
Alternatives to the Myers Briggs Chart
While the Myers Briggs Chart is a popular personality assessment, there are several alternatives that offer different perspectives on personality and behavior. Some of these include:
- Big Five Personality Traits: This model assesses personality based on five dimensions: Openness, Conscientiousness, Extraversion, Agreeableness, and Neuroticism.
- DISC Assessment: This tool measures four primary personality traits: Dominance, Influence, Steadiness, and Conscientiousness.
- Enneagram: The Enneagram is a model that categorizes personality into nine interconnected types, each with its own motivations and fears.
Each of these assessments offers unique insights into personality and can complement the understanding gained from the Myers Briggs Chart.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the Myers Briggs Chart used for?
The Myers Briggs Chart is used for understanding personality types, improving communication, enhancing personal development, and fostering better relationships.
2. How accurate is the Myers Briggs Assessment?
The accuracy of the Myers Briggs Assessment depends on the individual's self-awareness and honest responses. While it provides valuable insights, it's not a definitive measure of personality.
3. How do I find out my Myers Briggs personality type?
You can find out your Myers Briggs personality type by taking the MBTI assessment online or through a certified practitioner.
4. Can the Myers Briggs Chart be used in the workplace?
Yes, the Myers Briggs Chart is widely used in the workplace for team building, leadership development, and improving communication and collaboration.
5. Are there any criticisms of the Myers Briggs Chart?
Yes, some criticisms of the Myers Briggs Chart include concerns about its scientific validity, reliability, and oversimplification of human behavior.
6. What are some alternatives to the Myers Briggs Chart?
Alternatives to the Myers Briggs Chart include the Big Five Personality Traits, DISC Assessment, and Enneagram, each offering different perspectives on personality.
Conclusion
The Myers Briggs Chart stands as a valuable tool for understanding the complexities of human personality. By exploring the intricacies of the four dichotomies and 16 personality types, individuals can gain insights into their natural preferences and behaviors. While the MBTI has faced criticism, its applications in personal and professional development continue to resonate with millions worldwide.
Whether you're seeking self-discovery, career guidance, or improved relationships, the Myers Briggs Chart offers a framework for exploring the diverse spectrum of human personality. By embracing the differences in personality types, we can foster greater empathy, collaboration, and understanding in our interactions with others.
As we continue to navigate the complexities of the modern world, the Myers Briggs Chart remains a beacon of insight and growth, guiding individuals toward a deeper understanding of themselves and the people around them.
For more information on the Myers Briggs Chart and its applications, consider exploring reputable resources such as the Official Myers & Briggs Foundation.