Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide, often manifesting as red, itchy, and scaly patches on the skin. Knowing how to tell if you have psoriasis can be crucial in managing the condition effectively and improving your quality of life. This disease can appear at any age and affects both genders equally, although it is most commonly diagnosed in adults. It's important to understand the symptoms and seek professional medical advice if you suspect you have psoriasis.
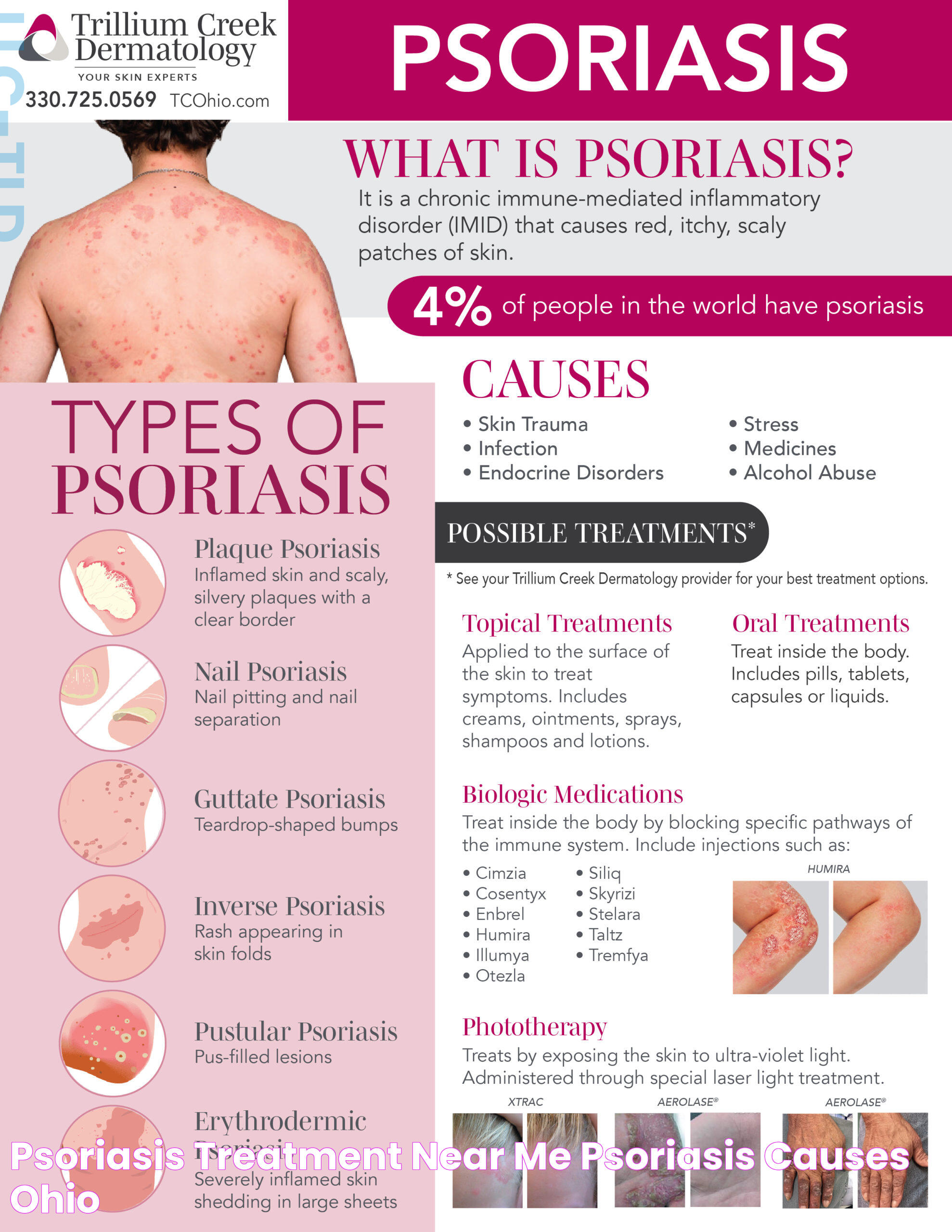
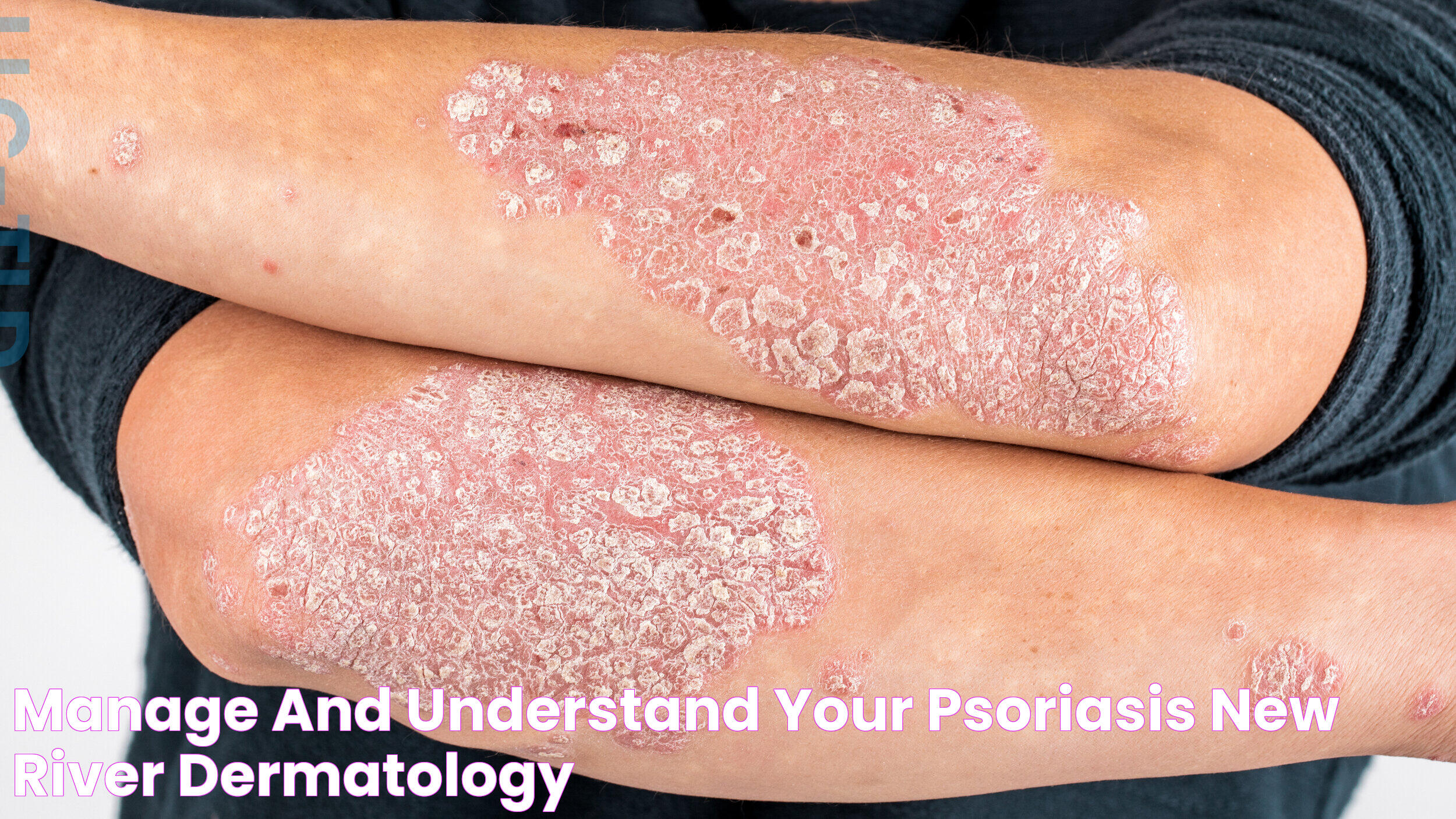
Identifying psoriasis involves recognizing its distinctive symptoms, which can vary from person to person. Common signs include red patches of skin covered with silvery scales, dry and cracked skin that may bleed, and itching or burning sensations. While these symptoms are typical of psoriasis, they can also resemble other skin conditions, making professional diagnosis essential. Understanding the different types of psoriasis and their unique symptoms can help you distinguish between them and seek appropriate treatment.
In addition to recognizing the symptoms, understanding the causes of psoriasis is equally important. This condition is believed to be an autoimmune disease, where the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells. Various factors, such as genetics, environmental triggers, and lifestyle choices, can contribute to the development of psoriasis. By learning more about these factors, you can take proactive steps to manage your condition and reduce the frequency and severity of flare-ups.
Read also:Renowned Surnames Of Prosperity The Legacy Of Rich People Last Names
Table of Contents
- What is Psoriasis?
- Symptoms of Psoriasis
- How to Tell if You Have Psoriasis?
- Types of Psoriasis
- Causes of Psoriasis
- Diagnosis of Psoriasis
- Risk Factors
- Treatment Options
- Managing Psoriasis
- Lifestyle Changes
- Diet and Nutrition
- Coping with Psoriasis
- Psoriasis and Mental Health
- How Do I Know if My Skin Condition is Psoriasis?
- FAQs
- Conclusion
What is Psoriasis?
Psoriasis is a long-lasting, non-contagious autoimmune disease characterized by the rapid growth of skin cells. This accelerated skin growth results in red, scaly patches that can appear anywhere on the body but are most commonly found on the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back. Psoriasis can be mild, moderate, or severe, affecting small areas or widespread regions of the skin.
Symptoms of Psoriasis
The symptoms of psoriasis can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. However, some common symptoms include:
- Red patches of skin covered with thick, silvery scales
- Dry, cracked skin that may bleed or itch
- Itching, burning, or soreness around the patches
- Thickened or ridged nails
- Swollen and stiff joints
It's important to note that psoriasis symptoms can come and go, with periods of remission followed by flare-ups.
How to Tell if You Have Psoriasis?
Determining if you have psoriasis can be challenging, as its symptoms can resemble other skin conditions such as eczema or dermatitis. Here are some steps to help you identify psoriasis:
- Examine your skin: Look for red patches with silvery scales, commonly found on the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back.
- Note any itching or discomfort: Psoriasis patches can cause intense itching or burning sensations.
- Check your nails: Psoriasis can cause nails to become thickened, pitted, or ridged.
- Observe joint pain: Some people with psoriasis also experience joint pain, a condition known as psoriatic arthritis.
If you suspect you have psoriasis, it's essential to consult a dermatologist for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
Types of Psoriasis
Psoriasis is not a one-size-fits-all condition; it comes in various forms, each with unique characteristics. The five main types of psoriasis include:
Read also:Do Dinosaurs Appear In The Bible Uncover Biblical Mysteries
- Plaque Psoriasis: The most common form, characterized by raised, red patches covered with a buildup of dead skin cells.
- Guttate Psoriasis: Often starts in childhood or young adulthood, featuring small, dot-like lesions.
- Inverse Psoriasis: Manifests as bright red lesions that appear in skin folds.
- Pustular Psoriasis: Characterized by white pustules surrounded by red skin.
- Erythrodermic Psoriasis: A severe form that leads to widespread, fiery redness over most of the body.
Causes of Psoriasis
The exact cause of psoriasis remains unclear, but it's believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Some key factors include:
- Genetics: Psoriasis tends to run in families, indicating a genetic predisposition.
- Immune system: An overactive immune response causes the rapid growth of skin cells, leading to psoriasis symptoms.
- Environmental triggers: Factors such as stress, skin injuries, infections, and certain medications can trigger or worsen psoriasis.
Diagnosis of Psoriasis
Diagnosing psoriasis typically involves a thorough examination by a dermatologist. The diagnosis process may include:
- Physical Examination: The doctor examines your skin, scalp, and nails for signs of psoriasis.
- Medical History: Discuss your symptoms, family history, and any potential triggers with your doctor.
- Skin Biopsy: In some cases, a small sample of skin is taken for laboratory analysis to confirm the diagnosis.
Risk Factors
Certain factors may increase your risk of developing psoriasis, including:
- Family history: A close relative with psoriasis increases your risk.
- Viral and bacterial infections: Conditions such as strep throat can trigger psoriasis.
- Stress: High-stress levels can exacerbate psoriasis symptoms.
- Obesity: Excess weight increases the likelihood of psoriasis developing in skin folds.
- Smoking: Tobacco use is linked to a higher risk of developing psoriasis.
Treatment Options
While there is no cure for psoriasis, several treatment options can help manage symptoms and improve skin appearance. These include:
- Topical Treatments: Creams and ointments applied directly to the skin can reduce inflammation and scaling.
- Phototherapy: Exposure to ultraviolet light can slow the growth of affected skin cells.
- Systemic Medications: Oral or injected medications that affect the entire body can be used for severe cases.
- Biologics: These drugs target specific parts of the immune system to reduce psoriasis symptoms.
Managing Psoriasis
Effective management of psoriasis involves a combination of treatments and lifestyle changes. Consider the following tips:
- Follow your treatment plan: Adhere to your doctor's recommendations for medications and treatments.
- Moisturize regularly: Keeping your skin hydrated can reduce dryness and scaling.
- Avoid triggers: Identify and minimize exposure to factors that worsen your symptoms.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle: Eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and managing stress can improve your overall health and well-being.
Lifestyle Changes
Adopting certain lifestyle changes can complement medical treatments and help manage psoriasis more effectively:
- Smoking cessation: Quitting smoking can improve treatment outcomes and reduce flare-ups.
- Weight management: Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the severity of psoriasis symptoms.
- Stress management: Techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing can help manage stress.
Diet and Nutrition
While there is no specific diet for psoriasis, some dietary changes may help reduce symptoms:
- Anti-inflammatory foods: Incorporate foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts.
- Fruits and vegetables: A diet high in fruits and vegetables can support overall health and reduce inflammation.
- Limit alcohol: Alcohol can interfere with psoriasis treatments and exacerbate symptoms.
Coping with Psoriasis
Living with psoriasis can be challenging, but certain strategies can help improve your quality of life:
- Educate yourself: Learn about psoriasis and its management to make informed decisions about your care.
- Seek support: Connect with support groups or online communities for encouragement and advice.
- Communicate openly: Talk to your healthcare provider about any concerns or questions you have regarding your condition and treatment.
Psoriasis and Mental Health
Psoriasis can have a significant impact on mental health, leading to anxiety, depression, and self-esteem issues. It's essential to address these challenges by:
- Seeking professional help: Consider therapy or counseling to manage emotional challenges.
- Practicing self-care: Engage in activities that promote relaxation and well-being.
- Building a support network: Surround yourself with family and friends who understand and support your journey.
How Do I Know if My Skin Condition is Psoriasis?
Determining whether your skin condition is psoriasis requires careful observation and professional evaluation. Consider the following tips:
- Compare symptoms: Look for key indicators such as red patches with silvery scales and joint pain.
- Consult a dermatologist: A dermatologist can provide a definitive diagnosis based on a physical examination and medical history.
- Consider a biopsy: In uncertain cases, a skin biopsy can confirm the presence of psoriasis.
FAQs
- What triggers psoriasis flare-ups? Stress, infections, weather changes, and certain medications can trigger flare-ups.
- Is psoriasis contagious? No, psoriasis is not contagious and cannot be spread from person to person.
- Can diet affect psoriasis? While no specific diet cures psoriasis, anti-inflammatory foods may help reduce symptoms.
- Is psoriasis hereditary? Yes, genetics can play a role, and having a family history increases your risk.
- Can psoriasis affect mental health? Yes, psoriasis can impact mental health, leading to anxiety and depression.
- What is the best treatment for psoriasis? Treatment varies based on severity; options include topical treatments, phototherapy, and systemic medications.
Conclusion
Understanding how to tell if you have psoriasis is vital for managing the condition effectively. By recognizing the symptoms, understanding the causes, and seeking a proper diagnosis, you can work with healthcare professionals to develop a comprehensive treatment plan. With the right approach, individuals with psoriasis can lead fulfilling lives, minimizing the impact of the condition on their daily activities and overall well-being. Remember, managing psoriasis is a journey, and with the right tools and support, you can navigate it successfully.