Eczema, a chronic skin condition characterized by red, itchy, and inflamed patches, can be a source of significant discomfort and distress. For those living with eczema, finding effective treatment options is crucial to managing symptoms and improving quality of life. With a myriad of potential triggers and individual responses, understanding how to treat eczema is essential for achieving relief.
Despite being a common condition, many people struggle to find the right approach to manage their eczema. Treatments range from topical medications and lifestyle changes to natural remedies and dietary adjustments. The complexity of the condition necessitates a tailored approach that addresses individual needs and circumstances. This comprehensive guide will explore various strategies for treating eczema, providing insights into both conventional and alternative methods.
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in natural and holistic methods for managing eczema. These approaches not only focus on alleviating symptoms but also aim to address the root causes and promote overall skin health. By incorporating these strategies into daily routines, individuals can achieve long-term relief and reduce the frequency and severity of flare-ups. Read on to discover the best practices and solutions for how to treat eczema effectively.
Read also:Terrifying Bible Quotes Unearth The Chilling Verses
Table of Contents
- What is Eczema?
- Common Symptoms of Eczema
- Causes and Triggers of Eczema
- How to Treat Eczema?
- Topical Treatments
- Oral Medications
- Natural Remedies for Eczema
- Role of Diet and Nutrition
- Lifestyle Changes to Consider
- Managing Stress and Emotional Well-being
- Preventing Flare-Ups
- Eczema in Children: Special Considerations
- When to Seek Professional Help?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What is Eczema?
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by inflammation, redness, and itching of the skin. Often appearing in childhood, eczema can persist into adulthood and vary in severity. The condition is not contagious but can have a significant impact on daily life, affecting sleep, self-esteem, and overall well-being.
Eczema manifests differently in individuals, with some experiencing mild irritation and others suffering from severe flare-ups. The skin's barrier function is compromised in eczema, making it more susceptible to irritants and allergens. Understanding the nature of eczema is the first step in managing the condition effectively.
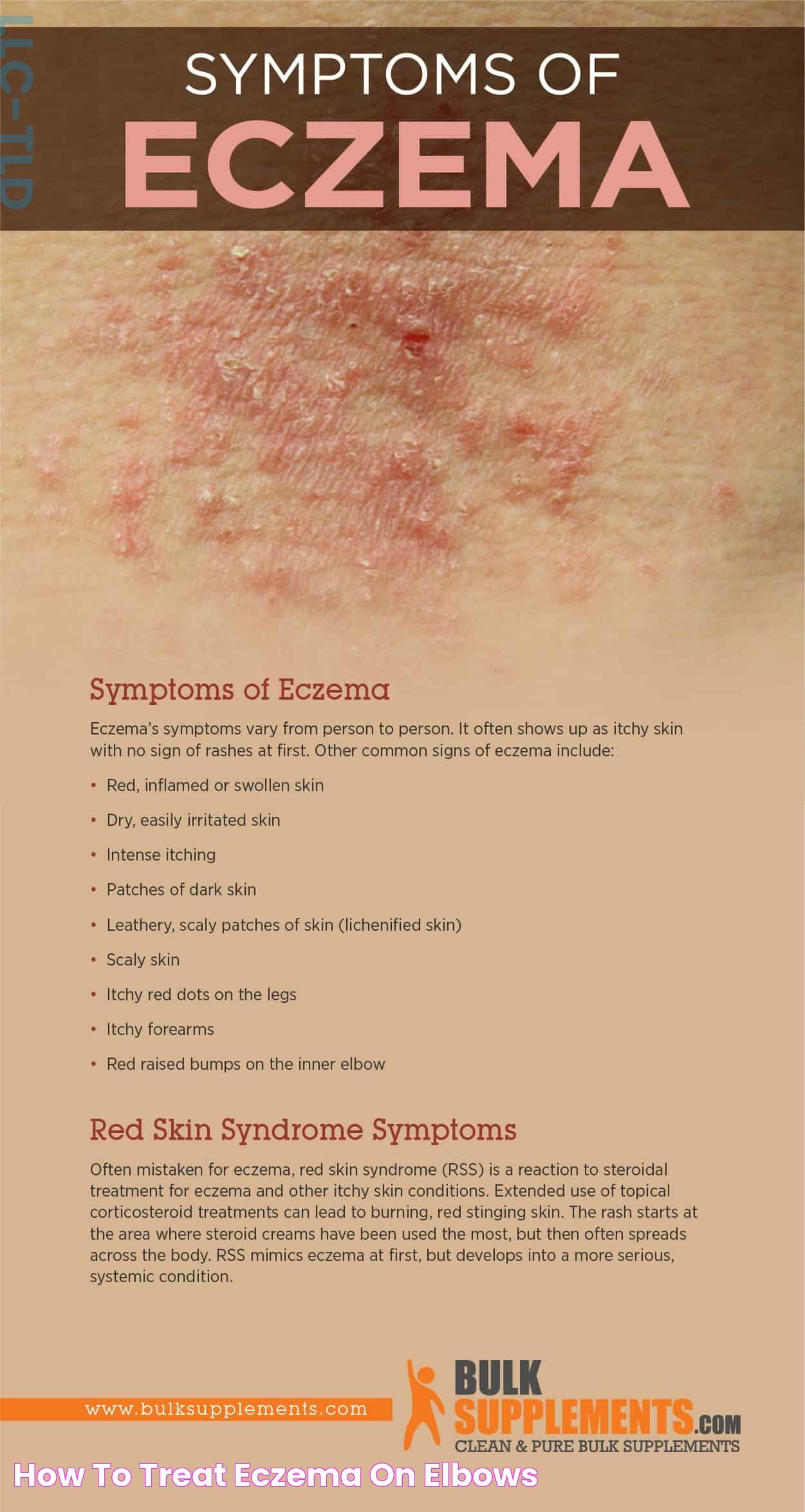
Common Symptoms of Eczema
The symptoms of eczema can vary but generally include:
- Intense itching, which may worsen at night
- Red or brownish-gray patches on the skin
- Small, raised bumps that may leak fluid when scratched
- Thickened, cracked, or scaly skin
- Inflamed skin that is sensitive to touch
These symptoms can appear anywhere on the body but are commonly found on the hands, feet, ankles, wrists, neck, upper chest, and eyelids. In infants, eczema often appears on the face and scalp. Identifying these symptoms early can help in seeking appropriate treatment and preventing further complications.
Causes and Triggers of Eczema
The exact cause of eczema is not fully understood, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Individuals with a family history of eczema, asthma, or hay fever are more likely to develop the condition. Environmental triggers may include:
- Exposure to irritants such as soaps, detergents, and fragrances
- Allergens like pollen, dust mites, and pet dander
- Temperature extremes and sweating
- Stress and emotional disturbances
- Infections, particularly viral infections
Identifying and avoiding triggers is crucial for managing eczema. Keeping a diary of flare-ups and possible triggers can aid in recognizing patterns and making necessary lifestyle adjustments.
Read also:Creative Friendship Tattoo Ideas Celebrate Your Bond With Style
How to Treat Eczema?
Treating eczema requires a multifaceted approach that combines medical treatments, lifestyle changes, and natural remedies. The primary goals are to alleviate symptoms, reduce inflammation, and prevent future flare-ups. Treatment plans should be tailored to individual needs and take into account the severity of the condition, age, and overall health.
Common strategies for treating eczema include:
- Using emollients and moisturizers to hydrate and protect the skin
- Applying topical corticosteroids to reduce inflammation
- Taking oral medications for severe cases
- Incorporating natural remedies and dietary changes
- Implementing lifestyle modifications to avoid triggers
It's important to work closely with healthcare professionals to determine the most effective treatment plan. Regular follow-up appointments can help monitor progress and make necessary adjustments.
Topical Treatments
Topical treatments are often the first line of defense against eczema. They are applied directly to the affected area to soothe and heal the skin. Common topical treatments include:
- Emollients: These are moisturizing treatments that help prevent dryness and protect the skin's barrier.
- Topical Corticosteroids: These anti-inflammatory creams or ointments are used to reduce swelling and redness.
- Calcineurin Inhibitors: Used for sensitive areas, these medications modulate the immune response to reduce symptoms.
Proper application of topical treatments is essential for their effectiveness. It's recommended to apply them immediately after bathing to lock in moisture. Patients should follow their healthcare provider's instructions for usage and duration.
Oral Medications
For individuals with moderate to severe eczema, oral medications may be prescribed to manage symptoms. These include:
- Antihistamines: These can help reduce itching, especially at night.
- Oral Corticosteroids: Used for short-term relief during severe flare-ups.
- Immunosuppressants: These are used to control the immune system and reduce inflammation.
Oral medications can have side effects and should be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional. It's important to discuss any concerns and have regular check-ups to monitor the treatment's impact.
Natural Remedies for Eczema
Many individuals seek natural remedies to complement conventional treatments. These remedies focus on soothing the skin and addressing underlying causes. Popular natural treatments include:
- Aloe Vera: Known for its soothing and anti-inflammatory properties.
- Coconut Oil: Moisturizes and reduces bacteria on the skin.
- Oatmeal Baths: Calms irritated skin and reduces itching.
- Tea Tree Oil: Offers antibacterial and anti-inflammatory benefits.
While natural remedies can be effective, it's important to test them on a small area of skin first to ensure there is no adverse reaction. Consulting with a healthcare provider before starting any new treatment is advisable.
Role of Diet and Nutrition
Diet and nutrition play a significant role in managing eczema. Certain foods can trigger flare-ups, while others may help reduce symptoms. Key dietary considerations include:
- Avoiding common allergens like dairy, eggs, and nuts
- Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods such as fatty fish, leafy greens, and berries
- Maintaining a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals
Keeping a food diary can help identify triggers and make necessary dietary adjustments. Working with a nutritionist can provide personalized guidance and support in managing eczema through diet.
Lifestyle Changes to Consider
Implementing lifestyle changes can significantly impact eczema management. Key changes include:
- Wearing loose, breathable clothing
- Using hypoallergenic skincare products
- Maintaining a regular skincare routine
- Reducing exposure to environmental triggers
Incorporating these changes into daily life can help minimize flare-ups and improve overall skin health. Consistency is key, and it may take time to see results.
Managing Stress and Emotional Well-being
Stress is a known trigger for eczema, and managing it is crucial for overall health. Techniques for reducing stress include:
- Practicing mindfulness and meditation
- Engaging in regular physical activity
- Seeking support from friends, family, or professionals
Addressing emotional well-being can have a positive impact on eczema symptoms and enhance quality of life. It's important to find strategies that work best for the individual.
Preventing Flare-Ups
Preventing eczema flare-ups involves a proactive approach. Strategies to consider include:
- Identifying and avoiding known triggers
- Maintaining a consistent skincare routine
- Staying hydrated and moisturizing regularly
By taking preventive measures, individuals can reduce the frequency and severity of flare-ups, leading to better management of the condition.
Eczema in Children: Special Considerations
Children with eczema require special care and attention. Parents can help by:
- Keeping the child's skin moisturized
- Using gentle, fragrance-free products
- Monitoring for signs of infection
- Educating the child about their condition
Working with a pediatric dermatologist can provide valuable guidance in managing eczema in children.
When to Seek Professional Help?
While many cases of eczema can be managed at home, professional help should be sought if:
- Symptoms are severe or worsening
- Over-the-counter treatments are ineffective
- There are signs of infection, such as pus or crusting
A dermatologist can provide a comprehensive evaluation and recommend appropriate treatments to manage eczema effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the best way to moisturize eczema-prone skin?
Use thick emollients or ointments immediately after bathing to lock in moisture.
- Can diet really affect eczema symptoms?
Yes, certain foods can trigger symptoms, while others may reduce inflammation.
- Are there any natural treatments for eczema?
Aloe vera, coconut oil, and oatmeal baths are popular natural remedies.
- Is stress management important in eczema treatment?
Yes, stress can trigger flare-ups, so managing it is crucial for treatment.
- How can I prevent eczema flare-ups?
Identify triggers, maintain a skincare routine, and keep skin hydrated.
- When should I see a dermatologist for eczema?
If symptoms are severe, worsening, or if there's an infection, seek professional help.
Conclusion
Treating eczema effectively requires a comprehensive and individualized approach that combines medical treatments, lifestyle changes, and natural remedies. Understanding how to treat eczema involves identifying triggers, maintaining a consistent skincare routine, and making dietary adjustments. With the right strategies in place, individuals can achieve relief from symptoms and improve their quality of life. It's important to work with healthcare professionals to tailor a treatment plan that meets individual needs and circumstances. By incorporating these strategies, individuals can manage eczema effectively and enjoy healthier skin.