Hair thinning is a concern that touches many lives, often leading to anxiety and confusion. Whether you notice more hair in your brush or a visible scalp, the reality of thinning hair can be distressing. Understanding the underlying causes is the first step toward finding a solution. With a myriad of contributing factors, identifying the specific reason for hair thinning can be challenging but necessary for effective treatment.
There are numerous reasons why your hair might be thinning. It could be due to genetics, medical conditions, nutritional deficiencies, or lifestyle choices. Each of these factors can impact hair health differently, necessitating a tailored approach to treatment. While some causes are temporary and reversible, others may require long-term management or professional intervention. Recognizing the signs early can help mitigate the impact and preserve your hair's vitality.
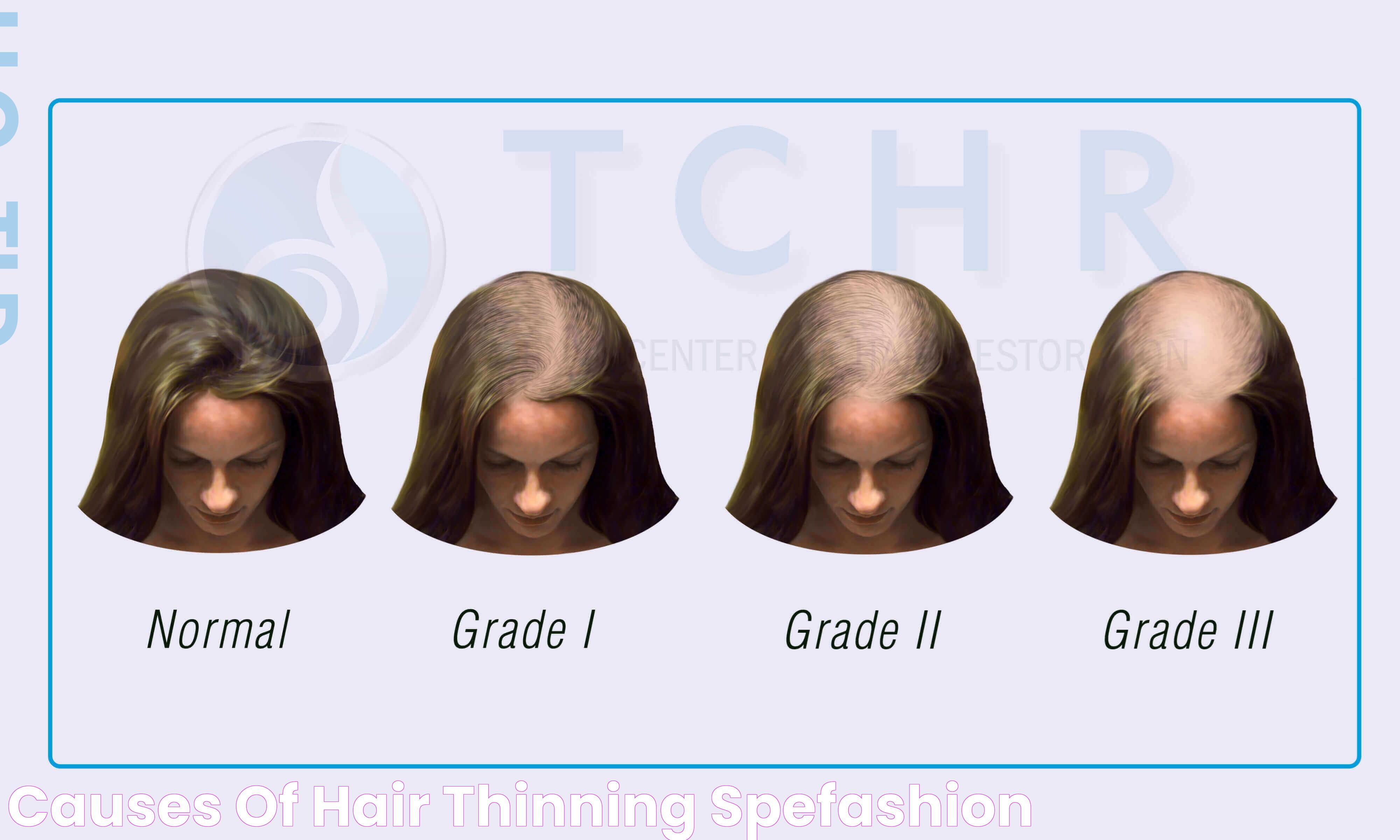
Hair thinning can occur at any age and affects both men and women. It’s crucial to differentiate between hair thinning and hair loss, as the two can manifest differently and might require distinct treatment strategies. By understanding the diverse causes and seeking appropriate guidance, you can navigate the challenges of hair thinning with confidence and optimism.
Read also:Enhancing Eloquence Words That Make You Sound Smart
Table of Contents
- Genetic Predisposition: Is It Inherited?
- Hormonal Changes and Hair Thinning
- Are Medical Conditions Causing Your Hair to Thin?
- Nutritional Deficiencies: What Are You Missing?
- Stress and Lifestyle: Their Impact on Hair Health
- Do Hair Care Products Contribute to Thinning?
- Scalp Health: Its Role in Hair Thinning
- Are Environmental Factors Affecting Your Hair?
- Age and Its Natural Impact on Hair Thinning
- What Are the Treatment Options for Thinning Hair?
- Dietary Changes to Combat Hair Thinning
- Is Medical Intervention Necessary?
- Exploring Natural Remedies for Hair Thinning
- Psychological Impact and Coping Strategies
- What Are the Future Trends in Hair Care?
Genetic Predisposition: Is It Inherited?
If you’re noticing that your hair is thinning, one of the first factors to consider is your genetic background. Hereditary hair loss, known as androgenetic alopecia, is the most common cause of hair thinning in both men and women. This condition can be inherited from either parent and tends to follow predictable patterns such as a receding hairline or thinning at the crown for men and diffuse thinning for women.
Genetic predisposition is influenced by a combination of genes, and certain ethnicities may be more susceptible to hereditary hair thinning. For example, Caucasian individuals often experience more pronounced thinning compared to Asians or Africans. Understanding your family history can provide insight into potential patterns and help you anticipate and address thinning hair more effectively.
Hormonal Changes and Hair Thinning
Hormonal fluctuations are another significant cause of hair thinning. Conditions such as pregnancy, menopause, and thyroid disorders can lead to hormonal imbalances that affect hair growth cycles. During pregnancy, increased levels of certain hormones can cause hair to appear thicker, but the postpartum period often sees a return to normal shedding patterns, sometimes resulting in noticeable thinning.
Menopause can bring about changes in hormone levels, particularly a decrease in estrogen, which may contribute to hair thinning. In men, an increase in dihydrotestosterone (DHT) can shrink hair follicles, leading to a gradual thinning of hair. Addressing hormonal imbalances through medical consultation and appropriate treatments can help manage hair thinning associated with these changes.
Are Medical Conditions Causing Your Hair to Thin?
Several medical conditions can lead to hair thinning, often as a symptom or side effect. Autoimmune disorders such as alopecia areata can cause the body’s immune system to attack hair follicles, resulting in patches of hair loss. Other conditions like lupus, anemia, and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can also contribute to thinning.
Chronic illnesses and treatments, such as chemotherapy for cancer, are known to cause significant hair loss. Additionally, certain medications, including those for hypertension, depression, and arthritis, may list hair thinning as a side effect. If you suspect a medical condition is affecting your hair, consulting a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation is essential.
Read also:The Remarkable Rise Of Jilly Anais A Star Beyond The Spotlight
Nutritional Deficiencies: What Are You Missing?
A balanced diet is crucial for maintaining healthy hair, and deficiencies in essential nutrients can lead to thinning. Iron deficiency is one of the most common causes of hair thinning; without adequate iron, the production of hair growth cells can be disrupted. Other vital nutrients include vitamins D, B12, and biotin, as well as minerals like zinc and selenium.
Crash diets, eating disorders, and poor dietary choices can exacerbate nutrient deficiencies. Ensuring a well-rounded diet rich in fruits, vegetables, proteins, and whole grains can support hair health. In some cases, supplementation may be necessary to address deficiencies and promote regrowth.
Stress and Lifestyle: Their Impact on Hair Health
Chronic stress is a well-known contributor to hair thinning. Stress can trigger conditions such as telogen effluvium, where hair prematurely enters the shedding phase. Major life events, trauma, or prolonged periods of anxiety can all lead to noticeable thinning.
Lifestyle choices, including smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and lack of exercise, can also negatively impact hair health. Incorporating stress-reduction techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, and regular physical activity can help mitigate the effects of stress on your hair.
Do Hair Care Products Contribute to Thinning?
Not all hair care products are created equal, and some may contribute to hair thinning. Products containing harsh chemicals, such as sulfates and parabens, can strip hair of its natural oils, leading to dryness and breakage. Overuse of styling tools and treatments like coloring, perming, or straightening can also weaken hair and cause thinning over time.
Choosing gentle, sulfate-free shampoos and conditioners, minimizing heat styling, and opting for natural hair care solutions can help protect your hair from further damage. Regular trimming and using protective hairstyles can also support hair health and reduce thinning.
Scalp Health: Its Role in Hair Thinning
The condition of your scalp plays a pivotal role in hair health. A healthy scalp provides a suitable environment for hair growth, while conditions like dandruff, psoriasis, or fungal infections can impede it. Excessive oil production or clogged hair follicles can also contribute to thinning hair.
Maintaining good scalp hygiene, using medicated shampoos if necessary, and keeping the scalp free from buildup can promote healthy hair growth. Regular scalp massages can increase blood circulation, providing the hair follicles with necessary nutrients and oxygen.
Are Environmental Factors Affecting Your Hair?
The environment can significantly impact hair health. Pollution, UV radiation, and exposure to harsh weather conditions can damage hair and contribute to thinning. Airborne pollutants can settle on the scalp and hair, causing irritation and weakening the hair shaft.
Protecting your hair from environmental stressors by wearing hats or scarves, using UV protection sprays, and washing hair regularly to remove pollutants can help mitigate these effects. Opting for natural and organic hair care products can further reduce exposure to harmful chemicals.
Age and Its Natural Impact on Hair Thinning
As we age, hair naturally undergoes changes, including thinning. The hair growth cycle slows down, and hair follicles shrink, leading to shorter, finer hairs. This process is a normal part of aging and can affect both men and women.
While age-related hair thinning is inevitable, maintaining a healthy lifestyle and using targeted hair care products can help slow the process. Incorporating products that promote volume and thickness can enhance the appearance of aging hair.
What Are the Treatment Options for Thinning Hair?
There are numerous treatment options available for those experiencing hair thinning. Topical treatments like minoxidil can stimulate hair growth, while oral medications such as finasteride may be prescribed for androgenetic alopecia. In some cases, hair transplant surgery may be a viable option for more severe thinning.
Alternative treatments, including laser therapy and platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy, have shown promise in promoting hair growth. Consulting a dermatologist or trichologist can help determine the most suitable treatment plan based on individual needs and conditions.
Dietary Changes to Combat Hair Thinning
Implementing dietary changes can be an effective way to address hair thinning. Ensuring a nutrient-rich diet with a focus on hair-friendly foods can support hair health. Foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and proteins are particularly beneficial for maintaining strong, healthy hair.
Incorporating foods like salmon, nuts, seeds, leafy greens, and eggs can help provide the nutrients necessary for hair growth. Staying hydrated and limiting processed foods and sugars can also contribute to improved hair health.
Is Medical Intervention Necessary?
Deciding whether medical intervention is necessary depends on the severity and underlying cause of hair thinning. In cases where thinning is due to medical conditions or hormonal imbalances, professional treatment may be required to address the root cause.
Regular check-ups with healthcare providers can help monitor health conditions that might contribute to hair thinning. Early intervention and personalized treatment plans can prevent further hair loss and promote regrowth.
Exploring Natural Remedies for Hair Thinning
For those seeking natural remedies, there are several options that may help with hair thinning. Essential oils like rosemary and peppermint have been shown to stimulate hair growth. Massaging these oils into the scalp can enhance circulation and promote healthy hair follicles.
Herbal supplements, such as saw palmetto and ginseng, may also support hair health. While natural remedies can be beneficial, it’s important to approach them with realistic expectations and consider them as part of a comprehensive hair care routine.
Psychological Impact and Coping Strategies
The psychological impact of hair thinning can be significant, affecting self-esteem and confidence. It’s important to address these feelings and seek support if needed. Joining support groups or speaking with a mental health professional can provide emotional relief and coping strategies.
Developing a positive self-image and focusing on aspects of appearance that bring joy and confidence can help mitigate the emotional toll of hair thinning. Embracing hairstyles and accessories that enhance individual beauty can also be empowering.
What Are the Future Trends in Hair Care?
The hair care industry continues to evolve, with innovations aimed at addressing hair thinning more effectively. Advances in technology, such as gene therapy and stem cell research, hold promise for future treatments. Personalized hair care products tailored to individual hair types and needs are also gaining popularity.
Staying informed about new developments and maintaining a proactive approach to hair care can help individuals manage hair thinning with optimism. Collaborating with professionals and exploring emerging trends can offer new opportunities for maintaining healthy hair.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Can hair thinning be reversed?
While some causes of hair thinning can be reversed, others may require ongoing management. Identifying the underlying cause is crucial for effective treatment and potential reversal. - How can I prevent my hair from thinning?
Maintaining a balanced diet, reducing stress, and using gentle hair care products can help prevent hair thinning. Regular check-ups with healthcare providers can also detect early signs of thinning. - What vitamins are best for hair growth?
Vitamins such as biotin, vitamin D, and B12 are often recommended for supporting hair growth and preventing thinning. - Are there any risks associated with hair transplant surgery?
As with any surgical procedure, hair transplant surgery carries risks such as infection, scarring, and unnatural-looking results. Consulting with a qualified professional is important. - How do I know if my hair thinning is due to genetics?
If you have a family history of hair thinning or baldness, it could be a genetic predisposition. Consulting with a dermatologist can provide a more accurate diagnosis. - Can stress alone cause hair thinning?
Yes, chronic stress can lead to conditions like telogen effluvium, resulting in noticeable hair thinning. Managing stress through healthy lifestyle choices can help mitigate its effects.