Severe PTSD can manifest in various ways, including flashbacks, nightmares, severe anxiety, and uncontrollable thoughts about the traumatic event. These symptoms can be debilitating and may lead to difficulties in functioning at work, in social settings, or even in maintaining personal relationships. It's important to recognize that severe PTSD is more than just a reaction to stress; it is a complex condition that requires comprehensive care and understanding from loved ones and mental health professionals alike. For individuals battling severe PTSD, the journey to recovery can be long and challenging, but it is not insurmountable. With the right combination of therapy, medication, and support, many people with severe PTSD can learn to manage their symptoms and regain control over their lives. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive overview of severe PTSD, exploring its causes, symptoms, treatment options, and the importance of seeking help. By shedding light on this condition, we hope to foster a greater understanding and empathy towards those who are affected by severe PTSD.
| Personal Details | Information |
|---|---|
| Name | Not Applicable |
| Age | Varies |
| Gender | All genders |
| Occupation | Varies |
| Diagnosis | Severe PTSD |
Table of Contents
- What is Severe PTSD?
- Causes of Severe PTSD
- Symptoms of Severe PTSD
- How Does Severe PTSD Affect Daily Life?
- Diagnosis of Severe PTSD
- Treatment Options for Severe PTSD
- Can Severe PTSD Be Cured?
- Coping Strategies for Severe PTSD
- Support for People with Severe PTSD
- How to Help Someone with Severe PTSD?
- Role of Family and Friends in Recovery
- Common Misconceptions About Severe PTSD
- Severe PTSD in Different Populations
- Future Research and Developments
- FAQs
- Conclusion
What is Severe PTSD?
Severe PTSD is a chronic mental health condition triggered by witnessing or experiencing a traumatic event. Unlike typical stress responses, severe PTSD involves persistent, intrusive symptoms that significantly impair daily functioning. These symptoms may include recurring flashbacks, hypervigilance, emotional numbness, and avoidance of reminders of the trauma.
The difference between PTSD and severe PTSD lies in the intensity and duration of symptoms. Severe PTSD symptoms are more pervasive, impacting multiple aspects of an individual's life. They often require specialized treatment and a comprehensive management plan for effective recovery. Understanding the nature of severe PTSD is vital for recognizing the need for professional intervention and support.
Read also:Cypress Location Guide A Detailed Exploration Of Geography And Culture
In severe cases, PTSD can lead to secondary mental health issues, such as depression, anxiety disorders, and substance abuse. This makes it imperative to address severe PTSD early and with evidence-based interventions to prevent further complications. By acknowledging the complexity of severe PTSD, we can better support those affected and work towards effective solutions.
Causes of Severe PTSD
Severe PTSD can stem from various traumatic events, including but not limited to:
- Military combat experiences
- Natural disasters
- Serious accidents
- Physical or sexual assault
- Witnessing violent incidents
The likelihood of developing severe PTSD is influenced by individual factors such as genetics, personal history, and the nature of the trauma. Some individuals may be more predisposed to developing PTSD due to hereditary factors or pre-existing mental health conditions. Additionally, the severity and duration of the traumatic event can also play a critical role in the onset of severe PTSD.
Understanding the causes of severe PTSD is essential for identifying those at risk and implementing preventive measures. Early recognition of symptoms and risk factors can lead to timely intervention, potentially mitigating the long-term effects of severe PTSD. Moreover, acknowledging the diverse causes of severe PTSD helps tailor treatment approaches to address the unique needs of each individual.
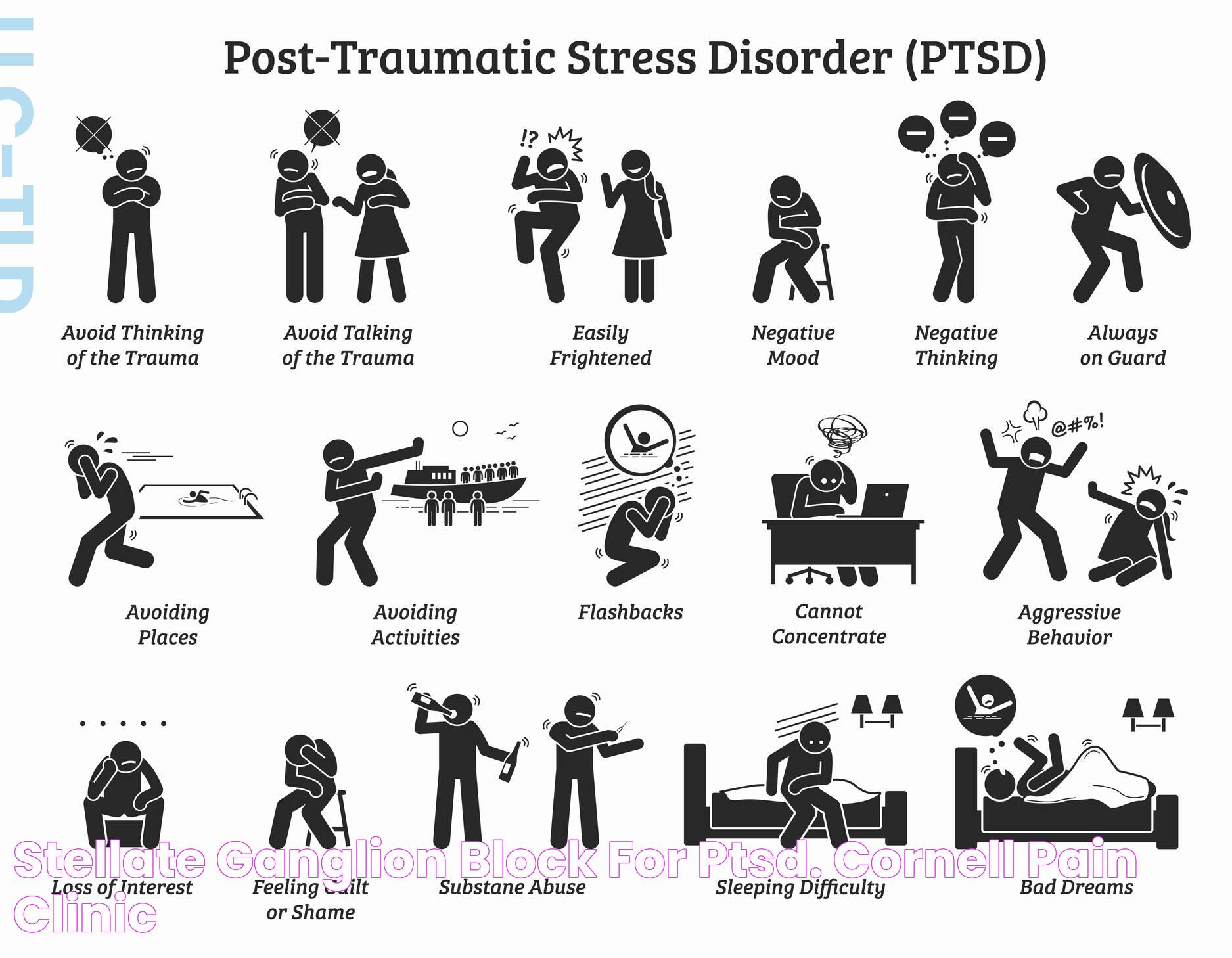
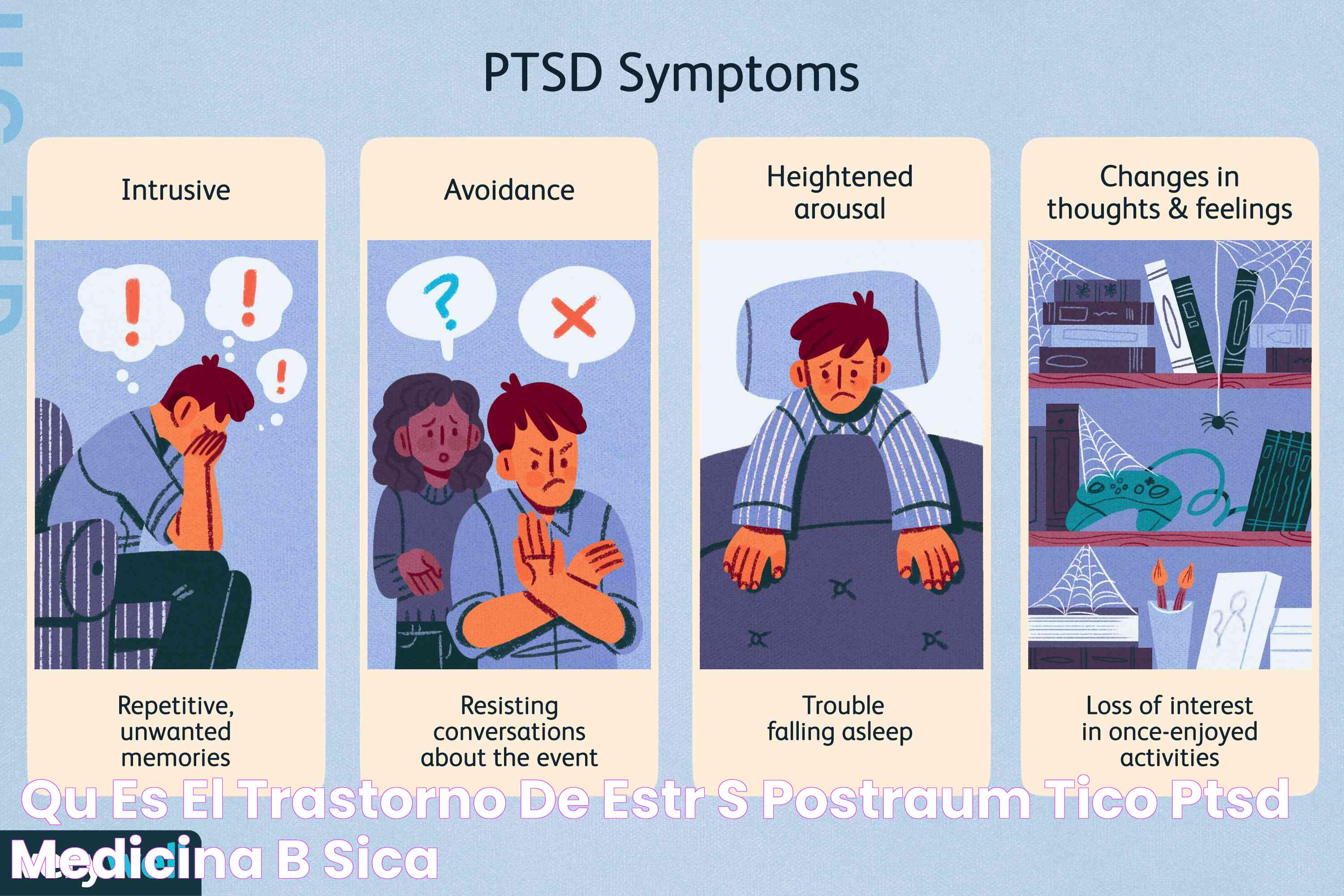
Symptoms of Severe PTSD
Severe PTSD symptoms are varied and can manifest differently in individuals. Common symptoms include:
- Intrusive thoughts: Frequent, distressing memories of the trauma
- Flashbacks: Reliving the traumatic event as if it were happening again
- Nightmares: Disturbing dreams related to the trauma
- Emotional distress: Feelings of intense fear, anger, or sadness
- Avoidance: Steering clear of places, people, or activities that remind one of the trauma
- Hyperarousal: Being easily startled or feeling tense and on edge
- Negative changes in mood and cognition: Experiencing negative thoughts, memory problems, or feelings of detachment
These symptoms can be debilitating, affecting a person's ability to function normally. Severe PTSD may also lead to self-destructive behaviors, such as substance abuse or self-harm, as individuals attempt to cope with their overwhelming emotions. Recognizing the symptoms of severe PTSD is crucial for seeking timely treatment and support.
Read also:Unraveling The Rich Heritage Of French Family Names
It's important to note that severe PTSD symptoms can fluctuate over time, often intensifying during periods of stress or when exposed to triggers. Therefore, ongoing management and support are essential for individuals with severe PTSD to maintain stability and improve their quality of life.
How Does Severe PTSD Affect Daily Life?
Severe PTSD can significantly disrupt an individual's daily life, impacting various aspects, including:
- Work: Difficulty concentrating, meeting deadlines, or interacting with colleagues
- Relationships: Struggles with communication, intimacy, or trust within personal relationships
- Social Life: Avoidance of social gatherings or withdrawal from social activities
- Physical Health: Developing chronic health issues due to stress or neglect of self-care
The pervasive nature of severe PTSD symptoms can lead to a cycle of avoidance and isolation, further exacerbating feelings of loneliness and despair. This can result in a decline in overall well-being, making it challenging for individuals to maintain a balanced and fulfilling life. Understanding the impact of severe PTSD on daily life highlights the importance of comprehensive treatment plans that address both emotional and practical challenges.
Moreover, severe PTSD can affect not only the individual but also their loved ones. Family members and friends may feel helpless or overwhelmed by the changes in behavior and mood of the person with PTSD. Providing education and support to those around someone with severe PTSD is crucial for fostering a supportive environment that encourages recovery and healing.
Diagnosis of Severe PTSD
Diagnosing severe PTSD involves a thorough evaluation by a mental health professional. This process typically includes:
- Clinical interviews: Discussing the individual's symptoms, history, and the impact on daily life
- Psychological assessments: Using standardized questionnaires or tests to assess the severity of symptoms
Criteria for diagnosing severe PTSD are outlined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), which requires the presence of specific symptoms related to the trauma. These symptoms must persist for more than a month and cause significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning.
Accurate diagnosis is essential for developing an effective treatment plan tailored to the individual's needs. It also helps differentiate severe PTSD from other mental health conditions that may present with similar symptoms, such as depression or anxiety disorders. Early diagnosis can lead to more successful outcomes, allowing individuals to access the necessary resources and support for their recovery journey.
Treatment Options for Severe PTSD
Treating severe PTSD often involves a combination of therapeutic approaches and, in some cases, medication. Common treatment options include:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Aims to change negative thought patterns and behaviors related to the trauma
- Exposure Therapy: Helps individuals confront and process traumatic memories in a controlled environment
- Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR): Utilizes guided eye movements to help individuals process and integrate traumatic memories
- Medications: Antidepressants or anti-anxiety medications may be prescribed to manage symptoms
Each treatment plan is individualized, taking into account the severity of symptoms, the individual's preferences, and their overall health. It's important for individuals with severe PTSD to work closely with their mental health provider to find a treatment approach that works best for them.
In addition to traditional therapies, alternative treatments such as mindfulness, yoga, or art therapy may also be beneficial for some individuals. These approaches can complement standard treatments by promoting relaxation, self-expression, and emotional regulation.
Can Severe PTSD Be Cured?
While there is currently no definitive cure for severe PTSD, many individuals can achieve significant symptom reduction and lead fulfilling lives with appropriate treatment and support. The goal of treatment is to help individuals manage their symptoms, improve their quality of life, and regain a sense of control over their experiences.
Recovery from severe PTSD is a highly individual process, and progress can vary from person to person. Some individuals may experience complete remission of symptoms, while others may continue to manage residual effects over time. The key to successful management of severe PTSD lies in accessing appropriate care, maintaining a strong support network, and adopting healthy coping strategies.
It's important to remain hopeful and persistent in the pursuit of recovery. With ongoing treatment and support, individuals with severe PTSD can find ways to overcome challenges and build a meaningful and satisfying life beyond the trauma.
Coping Strategies for Severe PTSD
Developing effective coping strategies is essential for managing severe PTSD symptoms. Some helpful approaches include:
- Establishing a daily routine: Helps provide structure and predictability
- Practicing relaxation techniques: Such as deep breathing, meditation, or progressive muscle relaxation
- Engaging in physical activity: Regular exercise can reduce stress and improve mood
- Connecting with support networks: Reaching out to friends, family, or support groups for emotional support
- Setting achievable goals: Breaking tasks into manageable steps to prevent feeling overwhelmed
- Practicing self-compassion: Being kind to oneself and acknowledging progress
It's important for individuals with severe PTSD to work with their healthcare provider to identify coping strategies that are most effective for their unique needs. Incorporating these strategies into daily life can enhance resilience and improve overall well-being.
Experimenting with different techniques and remaining open to trying new approaches can also be beneficial. What works well for one person may not be as effective for another, so finding a personalized set of strategies is key to successful coping and recovery.
Support for People with Severe PTSD
Having a strong support system is crucial for individuals with severe PTSD. Support can come from various sources, including:
- Family and friends: Providing emotional support, understanding, and encouragement
- Support groups: Connecting with others who have similar experiences
- Mental health professionals: Offering guidance, therapy, and treatment plans
- Community resources: Access to services, such as housing, employment, or financial assistance
Support systems play a vital role in helping individuals with severe PTSD feel understood and validated. They can also provide practical assistance in navigating daily challenges and accessing necessary resources. Encouraging open communication and fostering a sense of belonging can significantly enhance the recovery process.
For individuals with severe PTSD, reaching out for support can be challenging, but it is a crucial step in the healing journey. By building and maintaining strong connections with others, those with severe PTSD can find strength and resilience to overcome obstacles and work towards recovery.
How to Help Someone with Severe PTSD?
Supporting a loved one with severe PTSD requires patience, empathy, and understanding. Here are some ways to offer help:
- Educate yourself: Learn about severe PTSD to better understand their experiences
- Listen actively: Offer a non-judgmental ear and validate their feelings
- Encourage treatment: Support their journey to seek professional help and attend therapy sessions
- Be patient: Recovery takes time, and setbacks are normal
- Encourage healthy habits: Promote self-care activities, such as exercise and relaxation techniques
It's important to remember that while support is valuable, it is not a substitute for professional treatment. Encourage your loved one to engage with mental health services and remain supportive throughout their recovery process.
Providing a supportive and understanding environment can make a significant difference in the life of someone with severe PTSD. By being present and compassionate, you can help them navigate their challenges and work towards healing and recovery.
Role of Family and Friends in Recovery
Family and friends play a pivotal role in the recovery process for individuals with severe PTSD. Their involvement can provide emotional support, practical assistance, and a sense of stability. Key roles include:
- Offering emotional support: Being a source of comfort and reassurance
- Assisting with daily tasks: Helping manage responsibilities, such as household chores or appointments
- Encouraging treatment adherence: Supporting therapy attendance and medication compliance
- Fostering a safe environment: Reducing stressors and triggers in the home
Effective communication is essential in maintaining a supportive relationship. Family and friends should strive to understand the unique needs of their loved one with severe PTSD and work collaboratively to create a nurturing environment that promotes healing.
Ultimately, the support of family and friends can be a powerful catalyst for recovery, providing individuals with severe PTSD the strength and encouragement needed to navigate their challenges and achieve lasting wellness.
Common Misconceptions About Severe PTSD
There are several misconceptions about severe PTSD that can hinder understanding and support for those affected. Some common myths include:
- PTSD only affects military veterans: While veterans are at high risk, severe PTSD can affect anyone who has experienced trauma.
- People with PTSD are violent: The majority of individuals with severe PTSD are not violent. Symptoms are often internalized, such as anxiety and depression.
- PTSD is a sign of weakness: PTSD is a mental health condition, not a character flaw. It results from the brain's response to traumatic events.
- PTSD is incurable: While severe PTSD can be challenging, many individuals experience significant improvement with treatment and support.
Dispelling these misconceptions is crucial for fostering empathy and understanding towards individuals with severe PTSD. By challenging stereotypes and promoting accurate information, we can create a more supportive and inclusive environment for those affected by this condition.
Severe PTSD in Different Populations
Severe PTSD can affect various populations, each with unique challenges and needs. Some groups at higher risk include:
- Military veterans: Exposure to combat and military-related trauma increases the risk of severe PTSD.
- First responders: Police officers, firefighters, and paramedics often encounter traumatic events in their line of work.
- Survivors of abuse: Individuals who have experienced physical, emotional, or sexual abuse may develop severe PTSD.
- Refugees and asylum seekers: Those fleeing war or persecution face significant trauma and stress.
Each population may require tailored approaches to treatment and support, taking into account cultural, social, and environmental factors. Understanding the diversity of experiences with severe PTSD can help ensure that interventions are effective and sensitive to the needs of different groups.
By addressing the specific challenges faced by these populations, we can improve access to care and support for individuals with severe PTSD, ultimately enhancing their recovery journey and quality of life.
Future Research and Developments
The field of PTSD research is continuously evolving, with ongoing studies aimed at improving our understanding of severe PTSD and developing more effective treatments. Future research directions may include:
- Exploring the neurobiological mechanisms of PTSD: Understanding how trauma affects brain function and structure
- Developing innovative therapies: Investigating new therapeutic approaches, such as virtual reality-based treatments
- Identifying genetic factors: Studying genetic predispositions to PTSD to inform personalized treatment approaches
- Improving treatment accessibility: Finding ways to make effective treatments more widely available to diverse populations
Continued research and advancements in the field of severe PTSD hold promise for improving outcomes and providing hope for individuals affected by this challenging condition. By embracing new knowledge and technologies, we can enhance our ability to support those on their path to recovery.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between PTSD and severe PTSD?
Severe PTSD is characterized by more intense and persistent symptoms that significantly impair daily functioning, whereas PTSD may involve milder symptoms that do not disrupt daily life as extensively.
2. How long does it take to recover from severe PTSD?
Recovery from severe PTSD varies for each individual and can take months or even years. Ongoing treatment and support are essential for managing symptoms and improving quality of life.
3. Is medication necessary for severe PTSD treatment?
Medication may be recommended for some individuals with severe PTSD to manage symptoms, but it is often used in combination with therapy and other treatment approaches.
4. Can children develop severe PTSD?
Yes, children can develop severe PTSD following a traumatic event. Symptoms may differ from those in adults, and specialized treatment is often required to address their unique needs.
5. Are there support groups for severe PTSD?
Yes, there are numerous support groups available for individuals with severe PTSD and their families. These groups offer a safe space for sharing experiences and receiving support from peers.
6. How can I support a loved one with severe PTSD?
You can support a loved one with severe PTSD by educating yourself about the condition, providing emotional support, encouraging treatment, and fostering a safe and understanding environment.
Conclusion
Severe PTSD is a complex and challenging condition that requires comprehensive care and understanding. By increasing awareness and promoting accurate information, we can support individuals with severe PTSD in their journey towards recovery. Through appropriate treatment, supportive relationships, and effective coping strategies, those affected by severe PTSD can find hope and healing, ultimately leading to improved well-being and quality of life.
Continued research and advancements in the field hold promise for further enhancing our understanding and treatment of severe PTSD. By working together as a community, we can create a more supportive and empathetic environment for individuals living with this condition, paving the way for a brighter future.
For more information and resources on severe PTSD, please visit NIMH: Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder.