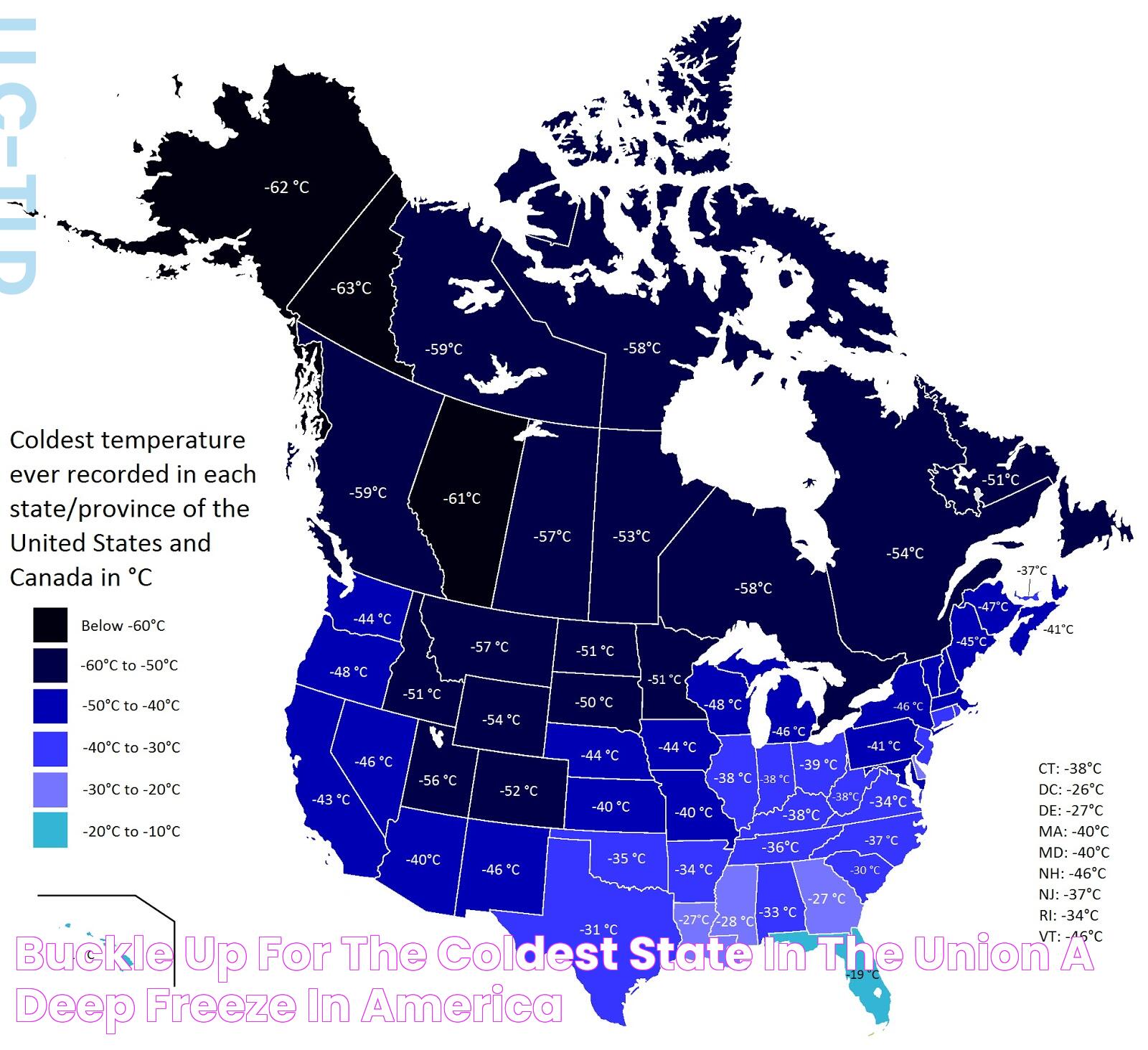
When one thinks of the coldest state in the US, Alaska undoubtedly comes to mind. Known for its breathtaking landscapes, majestic wildlife, and extreme temperatures, Alaska offers a unique experience to those who venture into its icy embrace. The vastness of this state, combined with its rich cultural history and natural wonders, makes it a compelling topic of interest for both researchers and travelers alike. But why is Alaska so cold, and how does it compare to other states in terms of climate?
Alaska's geographical position plays a significant role in its cold climate. Positioned at the northernmost point of the United States, it experiences long, harsh winters, with temperatures often plunging well below zero. The state's proximity to the Arctic Circle means it is subject to polar weather patterns, including long nights during the winter months and relatively cool summers. This unique climate has shaped the way of life for its inhabitants, impacting everything from transportation to architecture.
But Alaska is not just about cold temperatures. It is a land of contrasts, where icy landscapes coexist with warm-hearted communities and rich cultural traditions. From the indigenous peoples who have called this place home for thousands of years to the modern-day adventurers drawn by its untamed wilderness, Alaska is a state of resilience and adaptability. In this article, we will delve into the reasons behind Alaska's chilly reputation, explore its diverse ecosystems, and uncover the fascinating ways in which life thrives in the coldest state in the US.
Read also:Wanda Sykes Age A Deep Dive Into Her Life And Career
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Alaska's Climate
- Why is Alaska the Coldest State in the US?
- The Impact of Geography on Alaska's Climate
- How Does Alaska Compare to Other Cold States?
- The Coldest Cities in Alaska
- Wildlife of Alaska: Thriving in the Cold
- Human Adaptation to Cold: Living in Alaska
- Winter Activities in Alaska: Embracing the Cold
- Alaska's Indigenous Peoples and Their Connection to the Land
- Environmental Challenges Faced by Alaska
- Climate Change and Its Impact on Alaska
- The Role of Technology in Combatting Cold
- Alaska's Cultural Festivals: Celebrating the Cold
- FAQs About Alaska's Climate
- Conclusion: Embracing the Cold in Alaska
Introduction to Alaska's Climate
Alaska, the largest state in the US, is renowned for its extreme weather conditions. Its climate varies from region to region, with coastal areas experiencing milder temperatures compared to the harsh, frigid conditions of the interior. The state's climate can be classified into three main types: maritime, continental, and polar.
The maritime climate, found in the southern coastal regions, is characterized by relatively moderate temperatures and high precipitation. This is due to the influence of the Pacific Ocean, which helps to stabilize temperatures and create a more temperate environment.
In contrast, the continental climate of the interior is marked by extreme temperature variations, with scorching summers and bitterly cold winters. The lack of oceanic influence means that these areas can experience some of the coldest temperatures recorded in the United States.
Finally, the polar climate of northern Alaska is defined by long, dark winters and short, cool summers. This region, which includes the Arctic Circle, is known for its icy landscapes and unique weather patterns, such as the aurora borealis and midnight sun.
Why is Alaska the Coldest State in the US?
There are several factors that contribute to Alaska being the coldest state in the US. One of the primary reasons is its geographical location. Situated at the northernmost part of North America, Alaska is closer to the North Pole than any other state, resulting in colder temperatures.
Another factor is the state's topography. Alaska is home to numerous mountain ranges, including the Alaska Range and the Brooks Range, which can trap cold air and create frigid conditions. Additionally, the presence of large ice fields and glaciers further contributes to the cold climate.
Read also:Engaging Truth Or Drink Questions For Unforgettable Conversations
The state's proximity to the Arctic Ocean also plays a role in its cold weather. The Arctic Ocean is covered by ice for most of the year, which reflects sunlight and helps maintain cooler temperatures in the surrounding areas.
Moreover, Alaska's high latitude means it receives less sunlight during the winter months, leading to longer nights and colder temperatures. The lack of solar energy during this time of year contributes to the extreme cold experienced throughout the state.
The Impact of Geography on Alaska's Climate
Geography plays a crucial role in shaping Alaska's climate. Its position near the Arctic Circle means that the state is subject to polar weather patterns, which include long, cold winters and short, cool summers. Additionally, the mountainous terrain of the region can influence local weather conditions, creating microclimates that vary greatly from one area to another.
The presence of the Alaska Range, for example, can create rain shadows, where one side of the mountain range receives significantly more precipitation than the other. This can lead to variations in temperature and weather patterns across the state.
The state's vast size also means that there are significant differences in climate between regions. Coastal areas tend to have milder temperatures due to the influence of the ocean, while inland regions experience more extreme temperature fluctuations.
Overall, the diverse geography of Alaska contributes to its reputation as the coldest state in the US, with its varied landscapes and weather patterns providing a unique environment for both wildlife and human inhabitants.
How Does Alaska Compare to Other Cold States?
When it comes to cold temperatures, Alaska stands out as the coldest state in the US. However, there are other states that also experience harsh winters and frigid conditions. Some of these states include Minnesota, North Dakota, and Montana.
Minnesota, for example, is known for its long, cold winters, with temperatures often dropping below zero. The state's northern location and proximity to Canada contribute to its chilly climate.
North Dakota is another state that experiences extreme cold, particularly in the winter months. Its flat terrain and lack of natural barriers allow Arctic air masses to move freely across the region, leading to bitterly cold conditions.
Montana, with its mountainous terrain, also experiences cold temperatures, particularly in the higher elevations. However, its climate is more variable than Alaska's, with warmer summers and milder winters in some areas.
Despite the cold conditions experienced in these states, Alaska remains the coldest, with its extreme temperatures and unique weather patterns setting it apart from the rest.
The Coldest Cities in Alaska
Alaska is home to some of the coldest cities in the United States, where temperatures can plummet to extreme lows during the winter months. One of the coldest cities in Alaska is Fairbanks, located in the interior of the state. Known for its long, harsh winters, Fairbanks often experiences temperatures dropping below -30°F (-34°C) during the coldest months.
Another cold city in Alaska is Barrow, also known as Utqiagvik. Situated above the Arctic Circle, Barrow experiences polar climate conditions, with long periods of darkness during the winter and temperatures frequently dipping below zero. The city's remote location and proximity to the Arctic Ocean contribute to its frigid climate.
Nome, located on the western coast of Alaska, is another city known for its cold weather. Although it experiences milder temperatures compared to cities in the interior, Nome still faces harsh winter conditions, with temperatures often falling below freezing.
Despite the extreme cold, these cities are home to resilient communities that have adapted to the challenging climate, making the most of the unique environment that Alaska has to offer.
Wildlife of Alaska: Thriving in the Cold
Alaska is home to a diverse array of wildlife that has adapted to the cold climate of the region. From the iconic polar bear to the majestic moose, these animals have developed unique adaptations to survive and thrive in the harsh conditions of the coldest state in the US.
Polar bears, for example, are well-suited to the cold Arctic environment, with thick layers of blubber and dense fur that provide insulation against the freezing temperatures. Their large paws also help them navigate the icy terrain and swim in the frigid waters of the Arctic Ocean.
Moose, on the other hand, are equipped with long legs and a thick coat that allows them to move through deep snow and withstand the cold temperatures of the Alaskan wilderness. These large herbivores are commonly found in the forests and wetlands of the state, where they feed on a variety of vegetation.
In addition to these iconic species, Alaska is home to a wide range of other wildlife, including caribou, wolves, and various bird species. Each of these animals has developed unique adaptations to survive in the cold climate, contributing to the rich biodiversity of the region.
Human Adaptation to Cold: Living in Alaska
Living in Alaska requires a unique set of adaptations to cope with the cold climate and harsh conditions. Residents of the coldest state in the US have developed various strategies to stay warm and comfortable during the long winters.
One of the key adaptations is the use of insulated clothing and footwear, which helps to retain body heat and protect against the cold temperatures. Layering is also an important technique, allowing individuals to adjust their clothing to suit the varying weather conditions.
In addition to clothing, Alaskans have adapted their homes and buildings to withstand the cold. Many homes are equipped with high-efficiency heating systems, such as furnaces and wood stoves, to provide warmth during the winter months. Proper insulation and weatherproofing are also essential to keep homes warm and energy-efficient.
Transportation in Alaska is another area where adaptation is necessary. Many residents rely on vehicles equipped with all-wheel drive and winter tires to navigate the icy roads. Snowmobiles and dog sleds are also popular modes of transportation in some areas, particularly in remote regions where roads may be impassable during the winter months.
Overall, the residents of Alaska have developed a range of adaptations to thrive in the cold climate, making the most of the unique environment that the state has to offer.
Winter Activities in Alaska: Embracing the Cold
Despite the cold temperatures, Alaska offers a wide range of winter activities for residents and visitors alike. From outdoor adventures to cultural experiences, there is no shortage of ways to embrace the cold and enjoy all that the state has to offer.
One of the most popular winter activities in Alaska is dog sledding. This traditional mode of transportation has become a popular recreational activity, allowing participants to experience the thrill of mushing through the snow-covered landscape. Many tour operators offer guided dog sledding tours, providing an opportunity to learn about the history and techniques of this unique sport.
Skiing and snowboarding are also popular winter activities in Alaska, with numerous ski resorts and backcountry trails offering a variety of options for all skill levels. The state's mountainous terrain and abundant snowfall make it a prime destination for winter sports enthusiasts.
For those seeking a more relaxed experience, ice fishing is a popular pastime in Alaska. With thousands of frozen lakes and rivers, there are plenty of opportunities to try your hand at catching fish through the ice. Many communities host ice fishing derbies and festivals, providing a fun and social atmosphere for anglers of all ages.
In addition to outdoor activities, Alaska is home to a vibrant cultural scene, with numerous festivals and events celebrating the state's unique heritage and traditions. From the Iditarod Trail Sled Dog Race to the World Ice Art Championships, there are plenty of opportunities to experience the culture and history of Alaska during the winter months.
Alaska's Indigenous Peoples and Their Connection to the Land
The indigenous peoples of Alaska have a deep connection to the land and have lived in harmony with the cold climate for thousands of years. The state's native communities, including the Inuit, Athabaskan, and Aleut peoples, have developed unique cultural traditions and practices that are closely tied to the natural environment.
One of the key aspects of indigenous life in Alaska is subsistence hunting and fishing. These activities provide essential food resources for native communities and are deeply rooted in cultural traditions. Many indigenous peoples rely on the land and sea for sustenance, harvesting fish, marine mammals, and game animals to support their families and communities.
In addition to subsistence activities, indigenous peoples in Alaska have developed a rich cultural heritage that includes storytelling, art, and music. Traditional practices, such as drumming and dancing, are important aspects of community life and are often performed at cultural gatherings and ceremonies.
The connection to the land is also reflected in the traditional knowledge and practices of indigenous peoples. Many native communities have a deep understanding of the natural environment and have developed sustainable practices for living in harmony with the land and its resources.
Overall, the indigenous peoples of Alaska have a unique and enduring relationship with the cold climate, shaped by centuries of adaptation and cultural traditions.
Environmental Challenges Faced by Alaska
Alaska's unique environment presents a range of challenges for both its residents and wildlife. The extreme cold, coupled with the remote and rugged terrain, can make living and traveling in the state difficult. However, there are also broader environmental challenges that impact Alaska and its inhabitants.
One of the primary challenges is climate change, which is having a significant impact on the state's environment. Rising temperatures and melting ice are affecting the delicate ecosystems of Alaska, with consequences for both wildlife and human communities. The loss of sea ice, for example, is impacting marine mammals such as polar bears and walrus, which rely on the ice for hunting and resting.
In addition to climate change, Alaska faces other environmental challenges, such as pollution and habitat destruction. The state's vast natural resources, including oil and gas, have led to increased industrial activity, which can have negative impacts on the environment. Oil spills, for example, can have devastating effects on marine and coastal ecosystems, while deforestation and land development can lead to habitat loss for wildlife.
Efforts to address these environmental challenges are ongoing, with initiatives focused on conservation, sustainable development, and climate adaptation. These efforts aim to preserve the unique environment of Alaska for future generations and ensure the continued survival of its diverse wildlife.
Climate Change and Its Impact on Alaska
Climate change is having a profound impact on Alaska, with rising temperatures and changing weather patterns affecting the state's environment and communities. As one of the fastest-warming regions in the world, Alaska is experiencing a range of climate-related challenges that require urgent attention.
One of the most visible impacts of climate change in Alaska is the melting of glaciers and sea ice. As temperatures rise, glaciers are retreating at an unprecedented rate, leading to rising sea levels and changes in freshwater availability. The loss of sea ice is also impacting marine ecosystems, with consequences for species such as polar bears and seals that rely on the ice for survival.
In addition to melting ice, Alaska is experiencing changes in weather patterns, with increased instances of extreme weather events such as storms and floods. These events can have devastating impacts on communities, particularly those in remote and vulnerable areas.
Climate change is also affecting the traditional way of life for many indigenous communities in Alaska. Changes in animal migration patterns and the availability of natural resources are impacting subsistence hunting and fishing, which are vital for the survival of these communities.
Efforts to address climate change in Alaska are focused on both mitigation and adaptation. Initiatives aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions, promoting renewable energy, and enhancing community resilience are essential for addressing the challenges posed by a changing climate.
The Role of Technology in Combatting Cold
Technology plays a crucial role in helping residents of Alaska combat the cold and adapt to the challenging climate. Advances in technology have made it easier for individuals and communities to stay warm, safe, and connected in the coldest state in the US.
One of the key technological advancements is in the area of heating and insulation. Modern heating systems, such as high-efficiency furnaces and heat pumps, provide reliable and cost-effective solutions for keeping homes warm during the winter months. Advancements in insulation materials and techniques have also improved the energy efficiency of buildings, reducing heat loss and lowering energy costs.
In addition to heating and insulation, technology has also improved transportation in Alaska. All-wheel drive vehicles, winter tires, and advanced safety features make it easier and safer to navigate the icy roads. Innovations in snow removal equipment and techniques have also improved road conditions, making travel more accessible during the winter months.
Communication technology has also played a role in connecting remote communities in Alaska. Satellite phones, internet access, and other communication tools have made it easier for residents to stay connected with the outside world, access information, and call for assistance in emergencies.
Overall, technology has played a significant role in helping Alaskans adapt to the cold climate, improving quality of life and making it easier to thrive in the unique environment of the state.
Alaska's Cultural Festivals: Celebrating the Cold
Despite the cold temperatures, Alaska is home to a vibrant cultural scene, with numerous festivals and events that celebrate the state's unique heritage and traditions. These festivals provide an opportunity for residents and visitors to come together and embrace the cold, enjoying the rich cultural diversity of the region.
One of the most well-known cultural festivals in Alaska is the Iditarod Trail Sled Dog Race. Held annually in March, this iconic event celebrates the history and tradition of dog sledding in Alaska, with mushers and their teams racing across the state from Anchorage to Nome. The Iditarod is a celebration of endurance, skill, and the strong bond between mushers and their dogs.
Another popular festival is the World Ice Art Championships, held in Fairbanks. This event showcases the incredible talent of ice sculptors from around the world, who create stunning works of art from blocks of ice. The festival attracts thousands of visitors each year, who come to marvel at the intricate and beautiful sculptures.
In addition to these major events, there are numerous local festivals and cultural gatherings throughout Alaska, celebrating everything from traditional music and dance to indigenous art and crafts. These festivals provide a unique opportunity to experience the culture and history of Alaska, while also enjoying the beauty of the winter landscape.
FAQs About Alaska's Climate
What is the coldest temperature ever recorded in Alaska?
The coldest temperature ever recorded in Alaska was -80°F (-62°C) in the city of Prospect Creek on January 23, 1971. This temperature is one of the lowest ever recorded in the United States.
How long is the winter season in Alaska?
Winter in Alaska varies depending on the region, but it generally lasts from October to April. In the northern regions, winter can be even longer, with snow and cold temperatures persisting into May or June.
Do all parts of Alaska experience extreme cold?
No, not all parts of Alaska experience extreme cold. Coastal regions, such as the southeastern panhandle and the Aleutian Islands, have milder climates due to the influence of the ocean. However, the interior and northern regions of the state experience much colder temperatures.
What are some common ways Alaskans stay warm during the winter?
Alaskans stay warm during the winter by wearing insulated clothing, using high-efficiency heating systems, and ensuring their homes are properly insulated. Layering clothing is also a common practice to adjust to changing weather conditions.
Is it possible to see the Northern Lights in Alaska?
Yes, Alaska is one of the best places in the world to see the Northern Lights, also known as the aurora borealis. The lights are most visible in the northern regions of the state, particularly during the winter months when the nights are longest.
What is the impact of climate change on Alaska's wildlife?
Climate change is impacting Alaska's wildlife by altering habitats, food availability, and migration patterns. Species such as polar bears and walrus are particularly vulnerable to changes in sea ice, while other animals may be affected by shifts in vegetation and prey availability.
Conclusion: Embracing the Cold in Alaska
Alaska, the coldest state in the US, is a land of extremes, where frigid temperatures and breathtaking landscapes coexist with vibrant communities and rich cultural traditions. Despite the challenges posed by the cold climate, Alaskans have adapted and thrived, embracing the unique environment and making the most of all that the state has to offer.
From the incredible wildlife that calls Alaska home to the resilient communities that have developed innovative ways to combat the cold, the state is a testament to the power of adaptation and resilience. As climate change continues to impact the region, efforts to preserve and protect Alaska's environment and way of life are more important than ever.
Ultimately, Alaska is a place of beauty and wonder, where the cold is not just a challenge to overcome, but a defining characteristic that shapes the culture, history, and identity of the state. By embracing the cold and all that it brings, Alaskans continue to thrive in this unique and remarkable part of the world.