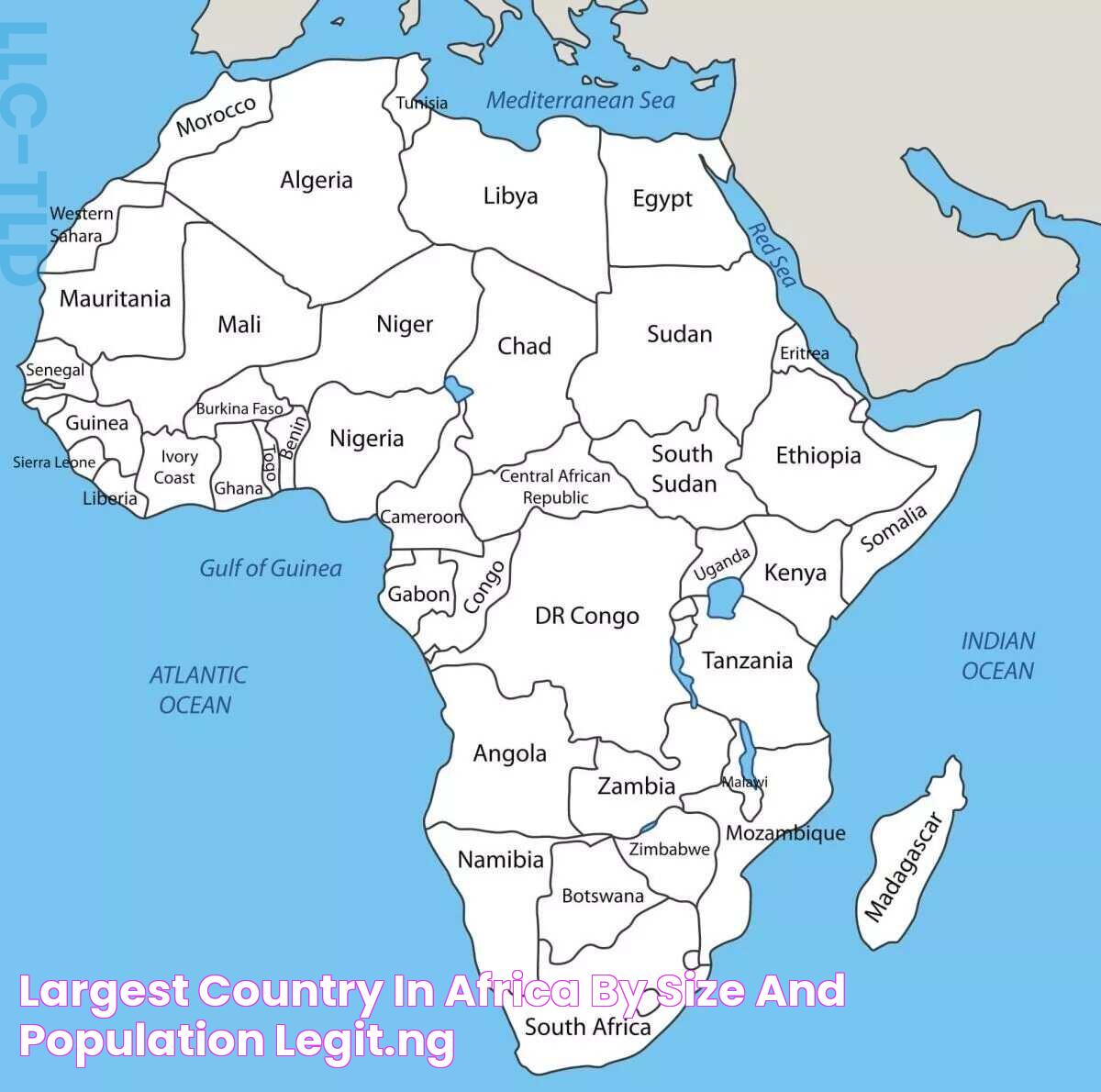
When pondering the question, "what is the largest country of Africa?" one may be surprised to learn that it is Algeria. Located in North Africa, Algeria boasts a vast expanse of land that stretches from the Mediterranean Sea to the heart of the Sahara Desert. This sprawling nation is not only the largest in Africa by land area but also holds a wealth of cultural, historical, and geographical treasures waiting to be explored. From its bustling cities to its serene desert landscapes, Algeria offers a unique blend of modernity and tradition that captivates the imagination.
Algeria's significance as Africa's largest country extends beyond its sheer size. Its strategic location has made it a crossroads of civilizations for centuries, influencing its diverse cultural tapestry. The country's rich history can be traced back to ancient times, with remnants of Roman, Byzantine, and Ottoman influences still visible today. Moreover, Algeria's abundant natural resources, including oil and gas, have positioned it as a key player in the global energy market, contributing to its economic growth and development.
In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the various facets of Algeria that make it such a remarkable nation. From its geographical features and climate to its vibrant culture and economy, we will explore the many aspects that define Algeria as the largest country in Africa. Whether you're a geography enthusiast, a history buff, or simply curious about this intriguing nation, read on to discover all that Algeria has to offer.
Read also:Andrew Form A Pioneering Force In The Entertainment Industry
Table of Contents
- Geographical Significance of Algeria
- A Brief Historical Overview of Algeria
- What Makes Algeria's Culture Diverse?
- Why is Algeria Considered an Economic Powerhouse?
- Understanding Algeria's Political Structure
- Exploring Algeria's Tourism Potential
- How Do Algeria's Natural Resources Impact Its Economy?
- Algeria's Climate and Environmental Challenges
- Who Are the People of Algeria?
- How Does Algeria's Education System Work?
- Algeria's Health Care System: An Overview
- What Is the State of Infrastructure in Algeria?
- Challenges Facing Algeria Today
- Algeria's Role in International Relations
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
Geographical Significance of Algeria
Algeria's geographical significance is underscored by its massive land area, which spans approximately 2.38 million square kilometers. This makes it not only the largest country in Africa but also the tenth largest in the world. The country's vast territory encompasses a diverse range of landscapes, from the fertile coastal plains along the Mediterranean Sea to the arid expanses of the Sahara Desert.
One of the key geographical features of Algeria is the Tell Atlas, a mountain range that runs parallel to the coast. This region is characterized by its Mediterranean climate, fertile soil, and lush vegetation, making it an important agricultural zone. In contrast, the southern part of the country is dominated by the Sahara Desert, which covers more than 80% of Algeria's land area. Despite its harsh conditions, the Sahara is home to a variety of unique ecosystems and wildlife.
The strategic location of Algeria has historically positioned it as a vital link between Africa and Europe. The country's Mediterranean coastline offers access to major shipping routes, facilitating trade and cultural exchange. Moreover, Algeria's proximity to other North African nations has allowed it to play a significant role in regional politics and economic cooperation.
A Brief Historical Overview of Algeria
Algeria's history is a rich tapestry woven with the influences of various civilizations that have left their mark on the land. The region's history dates back to prehistoric times, with evidence of early human habitation found in the Tassili n'Ajjer and Hoggar Mountains. These ancient rock art sites provide a glimpse into the lives of the early inhabitants of the Sahara.
Throughout history, Algeria has been a crossroads for various cultures and empires. The Phoenicians, Romans, Vandals, Byzantines, and Arabs have all left their imprint on the region. The Roman Empire, in particular, established several prosperous cities in Algeria, such as Timgad and Djemila, which are now UNESCO World Heritage Sites.
In the 16th century, Algeria became part of the Ottoman Empire, which lasted until the French colonization in 1830. The French colonial period had a profound impact on Algeria, shaping its political, social, and economic landscape. The struggle for independence culminated in the Algerian War of Independence, which lasted from 1954 to 1962, resulting in Algeria gaining its independence on July 5, 1962.
Read also:Exploration Of Diverse Shapes A Guide To Different Geometric Forms
What Makes Algeria's Culture Diverse?
Algeria's cultural diversity is a reflection of its complex history and the various peoples who have inhabited the region. The country's population is predominantly Arab-Berber, with the Berbers being the indigenous people of North Africa. Berber culture is characterized by its unique language, traditions, and music, which continue to thrive alongside Arab influences.
The influence of Islam is deeply embedded in Algerian culture, shaping the country's customs, values, and social norms. The majority of Algerians are Sunni Muslims, and Islamic festivals and rituals play a significant role in daily life. Traditional Algerian cuisine, music, and dance are also expressions of the country's cultural heritage, with dishes like couscous and tajine being popular staples.
Algeria's cultural diversity is further enriched by its vibrant arts scene, which includes traditional crafts such as pottery, weaving, and jewelry-making. The country's artistic heritage is also evident in its architecture, with a blend of Moorish, Ottoman, and French colonial styles visible in cities like Algiers and Oran.
Why is Algeria Considered an Economic Powerhouse?
Algeria's status as an economic powerhouse is largely attributed to its abundant natural resources, particularly oil and natural gas. The country is one of the largest producers of hydrocarbons in Africa and ranks among the top global exporters. The energy sector is a major driver of Algeria's economy, accounting for a significant portion of its GDP and government revenue.
In addition to its energy resources, Algeria has a diverse economy that includes agriculture, manufacturing, and services. The fertile coastal plains support the cultivation of various crops, including wheat, barley, and citrus fruits. Algeria's manufacturing sector encompasses industries such as textiles, cement, and electronics, while the services sector is bolstered by telecommunications, banking, and tourism.
The Algerian government has implemented various economic reforms to diversify the economy and reduce its dependence on hydrocarbons. These efforts include encouraging foreign investment, promoting entrepreneurship, and improving the business climate. Despite challenges such as unemployment and inflation, Algeria's economic potential remains significant, with opportunities for growth in sectors like renewable energy and technology.
Understanding Algeria's Political Structure
Algeria's political structure is defined by its status as a republic with a multi-party system. The country gained independence from France in 1962, and its current constitution was adopted in 1996. The President of Algeria serves as the head of state and is elected by popular vote for a five-year term, with the possibility of re-election.
The legislative branch of Algeria's government is bicameral, consisting of the People's National Assembly and the Council of the Nation. The People's National Assembly is composed of members elected by direct suffrage, while the Council of the Nation includes appointed and elected members. Together, these bodies are responsible for enacting legislation and overseeing the executive branch.
Algeria's judicial system is based on French civil law, with the Supreme Court serving as the highest court of appeal. The country has made efforts to strengthen the rule of law and promote transparency, although challenges such as corruption and bureaucratic inefficiencies persist.
Exploring Algeria's Tourism Potential
Algeria's tourism potential is immense, given its rich history, diverse landscapes, and cultural heritage. The country offers a wide range of attractions, from ancient archaeological sites to picturesque coastal towns and breathtaking desert vistas.
One of the most popular tourist destinations in Algeria is the capital city, Algiers, known for its blend of modernity and tradition. The city's Casbah, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, is a labyrinth of narrow streets, historic buildings, and markets that offer a glimpse into Algeria's past. Other notable attractions in Algiers include the Notre Dame d'Afrique basilica and the Martyrs' Memorial.
The Sahara Desert is another key attraction, drawing adventurers and nature enthusiasts from around the world. Visitors can explore the stunning sand dunes of the Erg Chebbi, visit the ancient rock art of Tassili n'Ajjer, or experience the unique lifestyle of the Tuareg people. The desert's vastness and tranquility provide a stark contrast to the bustling cities, offering a sense of solitude and reflection.
How Do Algeria's Natural Resources Impact Its Economy?
Algeria's natural resources are a cornerstone of its economy, particularly its vast reserves of hydrocarbons. The country is one of the leading producers of oil and natural gas in Africa, with significant deposits located in the Sahara Desert. The energy sector accounts for a substantial portion of Algeria's GDP, export earnings, and government revenue.
In addition to oil and gas, Algeria has other valuable natural resources, including minerals such as iron ore, phosphate, and zinc. The mining industry plays a role in the country's economy, although it is less developed compared to the energy sector. Efforts are underway to expand and diversify the mining industry to tap into Algeria's mineral wealth.
Algeria's abundant natural resources have attracted foreign investment, particularly in the oil and gas sector. The government has implemented policies to encourage exploration and development, including offering incentives to international companies. However, challenges such as fluctuating global energy prices and the need for infrastructure development remain.
Algeria's Climate and Environmental Challenges
Algeria's climate is characterized by a wide range of conditions, from the Mediterranean climate along the coast to the arid desert climate in the interior. The coastal regions experience mild, wet winters and hot, dry summers, making them ideal for agriculture. In contrast, the Sahara Desert is known for its extreme temperatures, with scorching heat during the day and chilly nights.
The diverse climate and geography present environmental challenges for Algeria, including water scarcity, desertification, and land degradation. The Sahara Desert's expansion poses a threat to agriculture and rural livelihoods, prompting efforts to combat desertification through reforestation and sustainable land management practices.
Climate change is another pressing issue for Algeria, with rising temperatures and changing precipitation patterns impacting the country's water resources and agriculture. The government is working to address these challenges through initiatives such as promoting renewable energy, improving water management, and enhancing climate resilience.
Who Are the People of Algeria?
Algeria is a diverse and multicultural nation, with a population of over 44 million people. The majority of Algerians are of Arab-Berber descent, with the Berbers being the indigenous people of North Africa. Berber communities can be found throughout the country, particularly in regions such as Kabylia, the Aurès Mountains, and the M'zab Valley.
Islam is the predominant religion in Algeria, with the majority of the population adhering to Sunni Islam. Islamic traditions and customs play a central role in Algerian society, influencing family life, education, and cultural practices. The official languages of Algeria are Arabic and Tamazight (Berber), with French also widely spoken, reflecting the country's colonial history.
Algeria has a youthful population, with a significant proportion under the age of 30. This demographic trend presents both opportunities and challenges, as the country seeks to harness the potential of its young workforce while addressing issues such as unemployment and education.
How Does Algeria's Education System Work?
Algeria's education system is structured into three main levels: primary, secondary, and higher education. Education is compulsory and free for children between the ages of 6 and 15, with the government placing a strong emphasis on ensuring access to quality education for all.
Primary education in Algeria lasts for five years, followed by four years of lower secondary education. Students then have the option to pursue upper secondary education, which can be either general or vocational. The Baccalauréat examination marks the completion of secondary education and serves as a prerequisite for university admission.
Higher education in Algeria is provided by universities, technical institutes, and specialized schools. The country has made significant investments in expanding its higher education sector, with a focus on increasing enrollment and improving the quality of education. However, challenges such as overcrowding, resource constraints, and the need for curriculum reform remain.
Algeria's Health Care System: An Overview
Algeria's health care system is a mix of public and private services, with the government playing a central role in providing health care to its citizens. The public health care system is funded by the state and offers free or low-cost services to the population, including primary, secondary, and tertiary care.
The country has made progress in improving health care access and outcomes, with efforts to expand health infrastructure, train medical personnel, and address communicable diseases. Algeria has also implemented programs to improve maternal and child health, reduce infant mortality, and combat non-communicable diseases.
Despite these achievements, the health care system faces challenges such as disparities in access between urban and rural areas, resource limitations, and the need for modernization. The government is working to address these issues through reforms, investments in health infrastructure, and partnerships with international organizations.
What Is the State of Infrastructure in Algeria?
Algeria's infrastructure development has been a priority for the government, with significant investments made in transportation, energy, and telecommunications. The country's strategic location and vast territory necessitate a well-developed infrastructure to support economic growth and regional integration.
The transportation sector has seen improvements in road networks, railways, and airports, facilitating the movement of goods and people across the country. Major projects, such as the East-West Highway and the Trans-Saharan Highway, have enhanced connectivity and trade opportunities.
Algeria's energy infrastructure is robust, with extensive networks for oil and gas production and distribution. The country is also investing in renewable energy, with plans to expand solar and wind power capacity to diversify its energy mix and reduce carbon emissions.
In the telecommunications sector, Algeria has made strides in expanding internet access and mobile connectivity, although challenges such as digital literacy and service quality persist. The government is working to address these issues through initiatives aimed at improving broadband infrastructure and promoting digital inclusion.
Challenges Facing Algeria Today
Despite its potential and resources, Algeria faces a range of challenges that impact its development and stability. Economic diversification is a key challenge, as the country seeks to reduce its dependence on hydrocarbons and develop other sectors such as agriculture, manufacturing, and tourism.
Unemployment, particularly among the youth, is another pressing issue, with efforts needed to create job opportunities and improve workforce readiness. The government is implementing policies to promote entrepreneurship, vocational training, and investment in emerging industries.
Political stability and governance are also areas of concern, with calls for reforms to enhance transparency, accountability, and citizen participation. The government has initiated measures to address these issues, although progress has been gradual.
Environmental challenges, such as climate change, water scarcity, and desertification, require coordinated efforts to ensure sustainable development and resilience. Algeria is working to address these challenges through initiatives focused on renewable energy, water management, and environmental conservation.
Algeria's Role in International Relations
Algeria plays a significant role in international relations, with its strategic location and resources positioning it as an important regional and global player. The country is a member of several international organizations, including the United Nations, African Union, Arab League, and Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC).
Algeria's foreign policy is characterized by principles of non-interference, peaceful resolution of conflicts, and support for self-determination. The country has been involved in mediating regional conflicts, promoting dialogue, and advocating for African unity and cooperation.
Economic diplomacy is a key aspect of Algeria's international relations, with efforts to strengthen trade ties, attract foreign investment, and participate in regional economic initiatives. The country is also working to enhance its cultural diplomacy, promoting its rich heritage and fostering people-to-people exchanges.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the largest country of Africa?
Algeria is the largest country in Africa, covering approximately 2.38 million square kilometers.
2. What are the main natural resources of Algeria?
Algeria's main natural resources include oil, natural gas, and minerals such as iron ore and phosphate.
3. What is the capital of Algeria?
The capital of Algeria is Algiers, a city known for its rich history and vibrant culture.
4. What languages are spoken in Algeria?
The official languages of Algeria are Arabic and Tamazight (Berber), with French also widely spoken.
5. What is the main religion in Algeria?
The main religion in Algeria is Islam, with the majority of the population adhering to Sunni Islam.
6. How does Algeria contribute to the global energy market?
Algeria is a major producer and exporter of oil and natural gas, contributing significantly to the global energy market.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Algeria stands as the largest country in Africa, not only in terms of land size but also in its rich cultural, historical, and economic significance. From its diverse geography and climate to its vibrant culture and strategic economic role, Algeria is a nation of contrasts and potential. As it navigates the challenges and opportunities of the modern world, Algeria continues to captivate with its unique blend of tradition and progress, offering a wealth of experiences for those who seek to explore its depths.