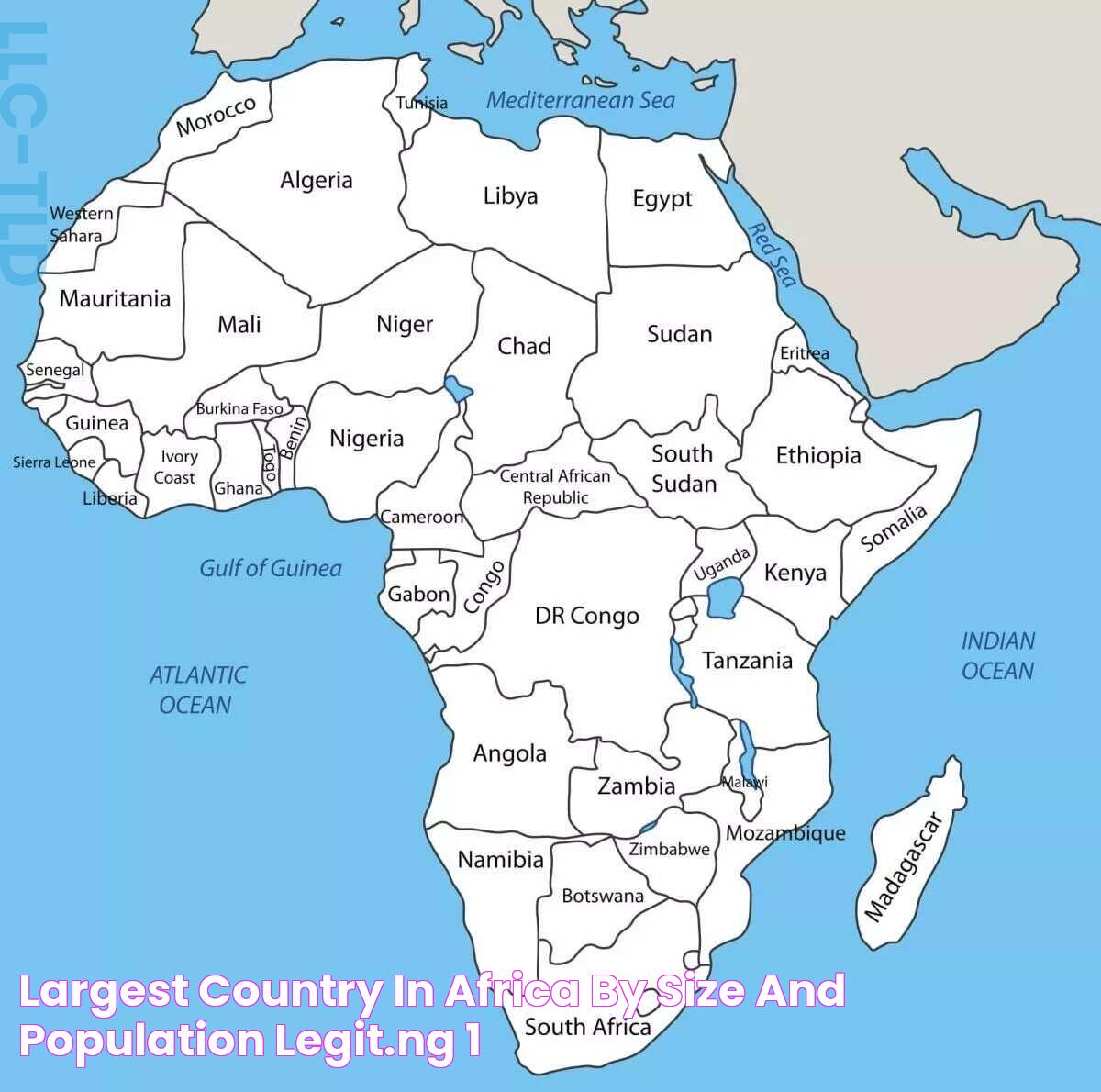
The African continent is known for its diverse landscapes, rich cultures, and vibrant histories. Among these, one country stands out due to its sheer size — Sudan, the largest country in Africa. With an area of approximately 1.86 million square kilometers, Sudan's vast expanse comprises deserts, mountains, and fertile lands. Its geographic grandeur is matched by its historical significance, having been a cradle of civilizations for millennia.
Sudan's size is not just a matter of geography; it is a pivotal player in the socio-political and economic fabric of Africa. The Nile River, running through its heart, has been a lifeline for the people of Sudan and has contributed to its agricultural prosperity. The country's rich resources, including minerals and oil, make it strategically significant on the African continent.
Despite its potential, Sudan faces challenges that impact its development. Political instability, economic pressures, and social issues have often overshadowed the country's strengths. However, Sudan's resilience and the spirit of its people continue to drive efforts toward peace and prosperity. This article delves into the multifaceted aspects of Sudan, shedding light on its geography, history, culture, and current affairs, painting a comprehensive picture of the largest country in Africa.
Read also:The Life And Influence Of Justin Combs Mom
Table of Contents
- What Makes Sudan Geographically Unique?
- Tracing the Historical Importance of Sudan
- Exploring the Cultural Mosaic of Sudan
- The Economic Potential of Sudan
- Decoding Sudan's Political Landscape
- What Are the Current Challenges Faced by Sudan?
- Sudan's Natural Resources: A Blessing or a Curse?
- How Does Agriculture Shape Sudan's Economy?
- Understanding the People and Society of Sudan
- Addressing Environmental Concerns in Sudan
- Sudan's Role in the African Continent
- What Is the Future Outlook for Sudan?
- Frequently Asked Questions about Sudan
- Conclusion: Sudan's Promise and Potential
What Makes Sudan Geographically Unique?
Sudan's geographical landscape is as diverse as it is vast. The country is bordered by seven nations, including Egypt to the north and South Sudan to the south. This strategic location has made Sudan a crossroads of cultures and civilizations.
The northern part of Sudan is dominated by the Sahara Desert, with its arid climate and sparse vegetation. This desert landscape is interspersed with oases that have historically served as vital points for trade and settlement.
Central and southern Sudan present a stark contrast, with fertile lands nourished by the Nile River and its tributaries. The Blue and White Niles converge in Khartoum, the capital, providing essential water resources that sustain agriculture and human settlements.
Furthermore, Sudan's Red Sea coastline offers access to maritime trade routes, bolstering its economic significance. The country's topography is punctuated by the Nuba Mountains and the expansive plains of Darfur, each contributing to Sudan's geographical diversity.
Climate and Seasons
The climate of Sudan varies significantly from north to south. The northern desert regions experience extreme temperatures, with scorching hot summers and mild winters. In contrast, the southern parts of Sudan receive more rainfall, supporting agriculture and dense vegetation.
Sudan has two main seasons: a dry season that lasts from October to April and a rainy season from May to September. These climatic variations influence agricultural cycles, water availability, and the overall lifestyle of the Sudanese people.
Read also:Sidney Crosby Age A Remarkable Journey In Hockey
Tracing the Historical Importance of Sudan
Sudan's historical narrative is deeply intertwined with the rise and fall of ancient civilizations. The Kingdom of Kush, one of the earliest civilizations, flourished along the Nile River around 1000 BCE. It was renowned for its powerful pharaohs, monumental pyramids, and rich cultural heritage.
The region's strategic location made it a hub for trade and cultural exchange between Africa, the Middle East, and the Mediterranean. Throughout the centuries, Sudan has witnessed the influence of various empires, including the Egyptian, Ottoman, and British empires, each leaving an indelible mark on its history.
The Impact of Colonialism
Colonialism profoundly impacted Sudan's political and social landscape. The British-Egyptian condominium rule in the late 19th and early 20th centuries significantly altered the country's governance structures. The quest for independence gained momentum in the mid-20th century, culminating in Sudan's independence in 1956.
Post-independence, Sudan faced numerous challenges, including civil conflicts and efforts to unify its diverse population under a cohesive national identity. These historical events have shaped Sudan's contemporary socio-political landscape.
Exploring the Cultural Mosaic of Sudan
Sudan's cultural heritage is a tapestry of diverse ethnicities, traditions, and languages. The country is home to over 500 ethnic groups, each with its unique customs and languages. This diversity is reflected in Sudan's vibrant arts, music, and culinary traditions.
The Nubian culture, with its rich history and architectural achievements, is an integral part of Sudan's cultural identity. The Nubian pyramids, located in the region of Meroe, are a testament to the kingdom's architectural prowess and are recognized as a UNESCO World Heritage site.
Languages and Traditions
Arabic is the official language of Sudan, but numerous indigenous languages are spoken across the country, reflecting its ethnic diversity. Traditional music and dance play a significant role in Sudanese culture, with genres like "Haqiba" music providing a rich auditory experience.
Cultural festivals, such as the Sufi processions and the Nubian Wrestling Festival, offer insights into Sudan's deep-rooted traditions and communal celebrations. These cultural expressions are pivotal in fostering a sense of unity and pride among the Sudanese people.
The Economic Potential of Sudan
Sudan's economy is primarily driven by agriculture, which employs a significant portion of the population. The fertile lands along the Nile River support the cultivation of crops such as sorghum, wheat, and millet. Livestock farming is also a crucial component of the rural economy.
In addition to agriculture, Sudan possesses substantial mineral resources, including gold, copper, and iron ore. The discovery of oil in the late 20th century further enhanced Sudan's economic prospects, although this sector has faced challenges due to geopolitical tensions and fluctuating oil prices.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite its potential, Sudan's economy faces numerous hurdles, including economic sanctions, inflation, and limited infrastructure. However, ongoing reforms and international collaborations offer opportunities for economic revitalization.
Efforts to diversify the economy, improve governance, and attract foreign investment are essential steps toward realizing Sudan's economic potential. The country's strategic location and abundant resources position it as a key player in regional trade and economic development.
Decoding Sudan's Political Landscape
Sudan's political history is marked by periods of conflict, transitions, and aspirations for democratic governance. The country's complex political landscape is characterized by its diverse ethnic groups and historical tensions between the north and south.
The Comprehensive Peace Agreement of 2005 marked a significant milestone in Sudan's political journey, leading to the independence of South Sudan in 2011. However, political instability and governance challenges continue to impact Sudan's progress.
Recent Political Developments
The ousting of former President Omar al-Bashir in 2019 ushered in a new era of political transition for Sudan. The establishment of a transitional government aimed at fostering peace and democratic reforms has been a critical step toward stability.
However, ongoing challenges such as internal conflicts, economic difficulties, and social unrest underscore the need for sustained efforts to achieve political stability and inclusive governance in Sudan.
What Are the Current Challenges Faced by Sudan?
Sudan's journey toward development is fraught with challenges that impact its socio-economic fabric. Political instability, economic sanctions, and inadequate infrastructure pose significant obstacles to progress.
Additionally, Sudan grapples with social issues such as poverty, healthcare access, and education disparities. These challenges are exacerbated by environmental concerns, including desertification and water scarcity.
Efforts for Resolution
Addressing these challenges requires collaborative efforts at national and international levels. Initiatives for peacebuilding, economic reforms, and social welfare programs are crucial steps toward overcoming these hurdles.
International support and partnerships with organizations such as the United Nations and the African Union play a vital role in facilitating Sudan's path to stability and development.
Sudan's Natural Resources: A Blessing or a Curse?
Sudan is endowed with abundant natural resources, including minerals, oil, and fertile lands. These resources have the potential to drive economic growth and improve living standards.
However, the management and equitable distribution of these resources remain contentious issues. Conflicts over resource control have often led to tensions and hindered development efforts.
Strategies for Sustainable Management
Sustainable management of natural resources is essential for Sudan's long-term development. Implementing transparent governance structures, promoting responsible mining practices, and investing in renewable energy sources are vital strategies.
By harnessing its natural resources responsibly, Sudan can pave the way for economic prosperity and environmental sustainability.
How Does Agriculture Shape Sudan's Economy?
Agriculture is the backbone of Sudan's economy, providing livelihoods for a significant portion of the population. The country's fertile lands, particularly along the Nile River, support the cultivation of various crops and livestock farming.
Sudan's agricultural sector faces challenges such as climate change, water scarcity, and outdated farming practices. However, advancements in agricultural technology and irrigation systems offer opportunities for enhancing productivity.
Future Prospects
Investing in modern agricultural techniques, promoting sustainable farming practices, and supporting rural development initiatives are crucial for strengthening Sudan's agricultural sector.
By capitalizing on its agricultural potential, Sudan can achieve food security, drive economic growth, and improve the livelihoods of its people.
Understanding the People and Society of Sudan
Sudan's society is a mosaic of diverse ethnic groups, each contributing to the country's rich cultural heritage. The Sudanese people are known for their resilience, hospitality, and communal spirit.
Family and community play a central role in Sudanese society, with traditions and customs passed down through generations. The country's social fabric is characterized by a strong sense of identity and pride in its cultural heritage.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite its cultural richness, Sudan faces social challenges such as poverty, education disparities, and healthcare access. Efforts to address these issues require collaborative approaches that empower communities and promote social cohesion.
By investing in education, healthcare, and social welfare programs, Sudan can enhance the well-being of its people and foster a more inclusive society.
Addressing Environmental Concerns in Sudan
Sudan's environment faces challenges such as desertification, water scarcity, and climate change. These issues impact agriculture, livelihoods, and the overall quality of life in the country.
Efforts to address environmental concerns include reforestation projects, sustainable water management, and climate adaptation strategies. These initiatives are essential for safeguarding Sudan's natural resources and ensuring a sustainable future.
International Collaboration
International partnerships and collaborations with organizations such as the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) are crucial for implementing effective environmental policies and programs in Sudan.
By fostering global cooperation, Sudan can address environmental challenges and build resilience against the impacts of climate change.
Sudan's Role in the African Continent
As the largest country in Africa, Sudan plays a significant role in regional politics, trade, and cultural exchanges. Its strategic location and abundant resources position it as a key player in the African Union and other regional organizations.
Sudan's contributions to peacekeeping efforts, conflict resolution, and regional development initiatives underscore its importance in the African continent's socio-political landscape.
Opportunities for Collaboration
Sudan's participation in regional collaborations and partnerships offers opportunities for economic growth, cultural exchange, and political stability. By fostering strong ties with neighboring countries and regional organizations, Sudan can enhance its role as a leader in Africa.
What Is the Future Outlook for Sudan?
Sudan's future is shaped by its ability to navigate challenges and capitalize on opportunities for growth and development. The country's journey toward stability and prosperity requires collaborative efforts at national, regional, and international levels.
Investing in infrastructure, education, and healthcare, along with promoting good governance and economic diversification, are essential steps toward realizing Sudan's potential.
Optimism for Progress
Despite the challenges, there is optimism for Sudan's future. The resilience and determination of the Sudanese people, coupled with international support, provide a foundation for positive change and development.
By embracing its rich cultural heritage and leveraging its natural resources, Sudan can pave the way for a brighter future for its people and the African continent.
Frequently Asked Questions about Sudan
- What is the largest country in Africa?
- What are the major languages spoken in Sudan?
- How does Sudan's climate vary across the country?
- What are Sudan's main economic activities?
- What cultural traditions are unique to Sudan?
- What challenges does Sudan face in terms of development?
Sudan is the largest country in Africa, with an area of approximately 1.86 million square kilometers.
Arabic is the official language of Sudan, but many indigenous languages are also spoken across the country.
Sudan's climate varies from arid desert in the north to tropical in the south, with distinct dry and rainy seasons.
Agriculture is the backbone of Sudan's economy, along with mining and oil production. The country is rich in natural resources.
Sudan boasts a rich cultural heritage, with unique music, dance, and festivals such as the Nubian Wrestling Festival and Sufi processions.
Sudan faces challenges such as political instability, economic sanctions, and environmental concerns, impacting its development efforts.
Conclusion: Sudan's Promise and Potential
Sudan, as the largest country in Africa, is a land of immense potential and promise. Its rich cultural heritage, abundant natural resources, and strategic location position it as a key player in the African continent.
While Sudan faces challenges in its journey toward stability and development, the resilience of its people and international support provide a foundation for progress. By embracing sustainable practices, fostering inclusive governance, and investing in its people, Sudan can achieve its aspirations and contribute to the prosperity of Africa.
As Sudan continues to navigate its path toward peace and prosperity, it remains a symbol of hope and opportunity, embodying the spirit of resilience and determination that defines the African continent.