Google, a name synonymous with the internet, is a powerhouse in the world of technology. It's a company that has transformed how we access information, communicate, and even think. But have you ever stopped to wonder who owns Google? Understanding the ownership structure of this tech giant not only sheds light on its business model and decision-making processes but also gives us insight into the people and entities steering the future of digital innovation.
In the world of corporate giants, ownership can often be complex and multifaceted. Google's ownership is no exception, involving a mix of founders, shareholders, and parent companies. This intricate web of ownership raises questions about control, influence, and the direction in which Google is headed. As one of the most influential companies globally, its ownership dynamics are a topic of immense interest and significance.
In this comprehensive article, we will explore the various facets of Google's ownership. We'll delve into the history of its founders, the role of its parent company Alphabet Inc., and the influence of major shareholders. Moreover, we'll examine how Google's ownership impacts its strategic decisions, innovation, and global reach. By the end of this journey, you'll have a clearer understanding of who truly owns Google and what this means for the future of technology.
Read also:Law Of Attraction Quotes Power Inspiration And Manifestation
Table of Contents
- History of Google: From Stanford to Global Dominance
- Who are the Founders of Google?
- Biography of Founders
- Google and Alphabet Inc.: What's the Relationship?
- Who are the Major Shareholders of Google?
- How Does Google Make Money?
- Google's Business Model Explained
- What is the Role of Shareholders in Google?
- Impact of Ownership on Google's Strategy
- What Does the Future Hold for Google?
- FAQs
- Conclusion
History of Google: From Stanford to Global Dominance
Google's story began in 1996 at Stanford University, where two Ph.D. students, Larry Page and Sergey Brin, embarked on a project to create a search engine that would organize the world's information and make it universally accessible and useful. What started as a research project quickly evolved into a business idea, leading to the official founding of Google Inc. on September 4, 1998.
The company's initial public offering (IPO) in 2004 was a significant milestone, marking its transformation from a university project into a publicly traded tech giant. The IPO raised over $1.67 billion, giving Google the financial muscle to expand its services and acquire other companies. Over the years, Google has diversified its offerings, including products such as Gmail, Google Maps, Android, and YouTube, establishing itself as a dominant player in the technology sector.
Today, Google is more than just a search engine. It is a subsidiary of Alphabet Inc., a multinational conglomerate that serves as Google's parent company. This restructuring, announced in 2015, allowed Google to focus on its core internet services while enabling Alphabet to manage its other business interests and experimental projects.
Who are the Founders of Google?
The minds behind Google are Larry Page and Sergey Brin, two computer science students from Stanford University. Their innovative approach to search engine technology, which involved ranking web pages based on the number and importance of links, set the stage for Google's success.
Page and Brin's partnership was instrumental in shaping Google's vision and culture. They shared a belief in the power of technology to change the world and were committed to maintaining Google's focus on innovation and user experience. Their leadership during Google's formative years was characterized by a commitment to creativity, risk-taking, and a "do no evil" philosophy.
Despite stepping down from their executive roles in 2019, Page and Brin remain significant figures within the company, both serving on Alphabet Inc.'s board of directors. Their influence continues to be felt, not just through their ownership stakes but also through the culture and values they instilled in Google.
Read also:Essential Traits Of Money Key Attributes And Their Significance
Biography of Founders
| Detail | Larry Page | Sergey Brin |
|---|---|---|
| Full Name | Lawrence Edward Page | Sergey Mikhaylovich Brin |
| Birthdate | March 26, 1973 | August 21, 1973 |
| Education | Stanford University (Ph.D., incomplete) | Stanford University (Ph.D., incomplete) |
| Role at Google | Co-founder, Former CEO | Co-founder, Former President |
| Current Role | Board Member, Alphabet Inc. | Board Member, Alphabet Inc. |
Google and Alphabet Inc.: What's the Relationship?
In 2015, Google underwent a major corporate restructuring that led to the formation of Alphabet Inc. This move was designed to streamline operations and allow Google to focus on its core internet services while Alphabet handled its other business ventures and research projects.
Alphabet Inc. became the parent company of Google, and its portfolio expanded to include other subsidiaries such as Calico, Nest, and Waymo. This reorganization provided greater transparency and flexibility, enabling each subsidiary to operate independently while benefiting from shared resources and expertise.
The relationship between Google and Alphabet is symbiotic. Google remains the most significant revenue generator for Alphabet, contributing the majority of its income through advertising and other services. Meanwhile, Alphabet supports Google's growth by investing in cutting-edge research and development in fields like artificial intelligence, healthcare, and autonomous vehicles.
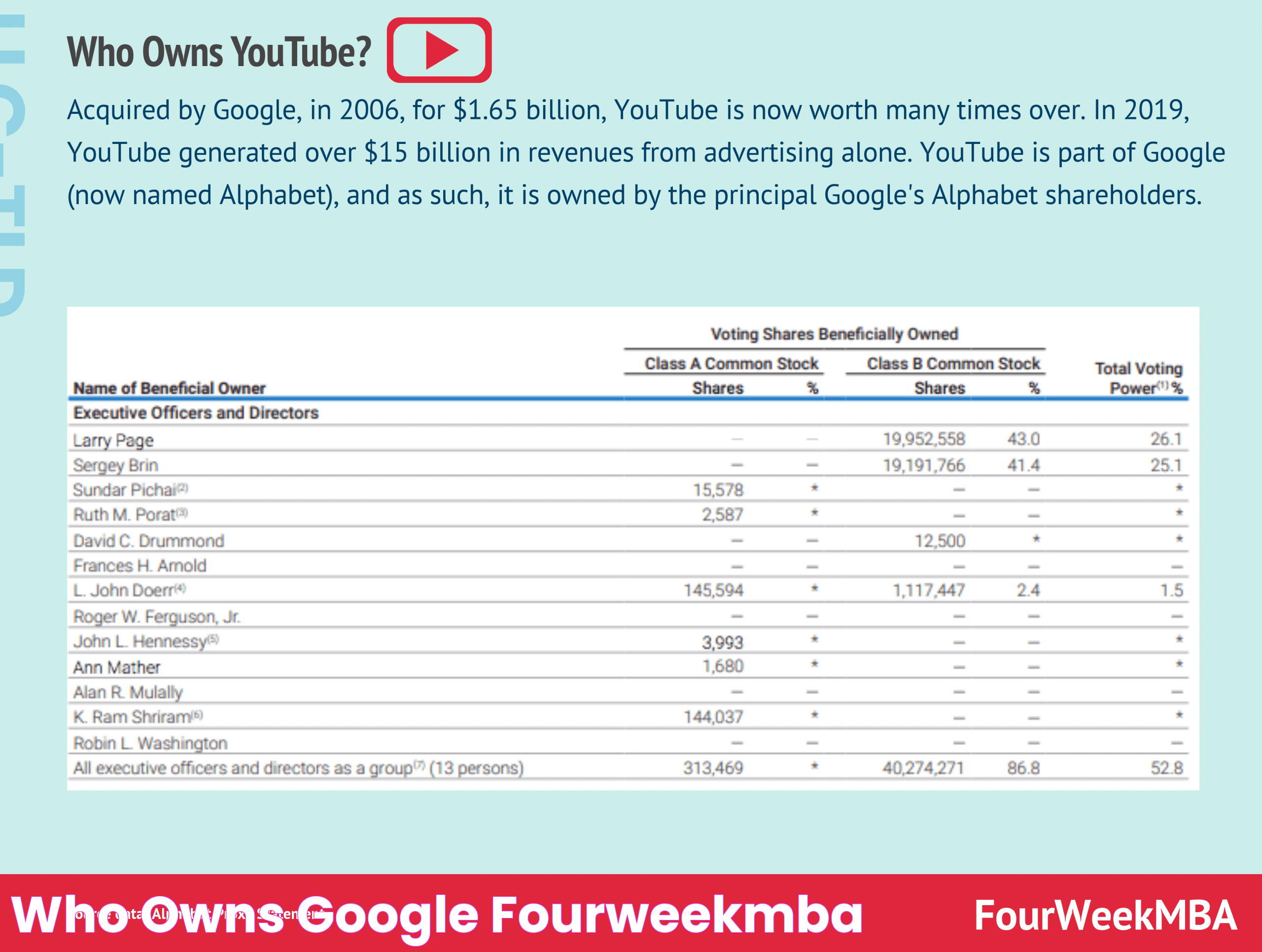
Who are the Major Shareholders of Google?
Google's ownership is distributed among a diverse group of shareholders, including its founders, institutional investors, and individual stockholders. The company's stock is publicly traded under Alphabet Inc., with two classes of shares: Class A (GOOGL) and Class C (GOOG).
Major shareholders include Larry Page and Sergey Brin, who retain significant voting power through their Class B shares, which are not publicly traded and carry ten times the voting rights of Class A shares. This structure allows them to maintain control over the company's strategic direction.
Institutional investors also hold substantial stakes in Alphabet, with investment firms like Vanguard Group and BlackRock among the top shareholders. These investors play a crucial role in shaping the company's policies and governance through their voting rights and influence.
How Does Google Make Money?
Google's revenue model is diverse, reflecting its wide range of products and services. The primary source of income is advertising, accounting for over 80% of its total revenue. Google's advertising platform, Google Ads, allows businesses to display ads on Google's search engine and its partner network, reaching billions of users worldwide.
In addition to advertising, Google generates revenue through other services, including:
- Cloud Computing: Google Cloud provides businesses with storage, computing power, and other services, contributing significantly to the company's income.
- Hardware: Google's hardware products, such as Pixel phones, Nest smart home devices, and Chromecast, add to its revenue streams.
- Subscriptions and Apps: Services like YouTube Premium, Google Play Store, and Google Workspace offer subscription-based revenue.
This diversified revenue model allows Google to invest in innovation and expansion, maintaining its competitive edge in the technology sector.
Google's Business Model Explained
Google's business model is built around providing free services to users while monetizing their attention through advertising. This model is based on the principle of attracting a large user base by offering valuable services, such as search, email, and maps, at no cost.
The company's advertising platform is highly effective due to its ability to target ads based on user behavior, interests, and demographics. This precision makes Google's advertising services attractive to businesses looking to reach specific audiences, driving high demand and revenue.
In addition to advertising, Google's business model includes diversification into other areas, such as cloud computing, hardware, and content creation. This diversification helps mitigate risks associated with relying solely on advertising revenue and positions Google for long-term growth.
What is the Role of Shareholders in Google?
Shareholders play a crucial role in Google's corporate structure and governance. They provide capital through the purchase of shares, enabling the company to invest in new projects, research, and expansion. In return, shareholders receive dividends and have the potential for capital gains through stock price appreciation.
Shareholders also have a say in Google's decision-making processes through voting rights. Important issues, such as the election of board members, mergers, and acquisitions, are often subject to shareholder approval. This gives them a degree of influence over the company's strategic direction.
However, due to the dual-class share structure, Google's founders retain significant control, allowing them to steer the company according to their vision while balancing shareholder interests.
Impact of Ownership on Google's Strategy
Google's ownership structure, characterized by the founders' control through Class B shares, has a profound impact on its strategic direction. This structure allows Larry Page and Sergey Brin to prioritize long-term innovation over short-term profits, fostering a culture of experimentation and risk-taking.
The influence of major shareholders, including institutional investors, also plays a role in shaping Google's strategies. These stakeholders often push for sustainable growth, transparency, and ethical business practices, aligning Google's interests with broader societal values.
This unique ownership dynamic has enabled Google to maintain its leadership position in the tech industry, continuously evolving and adapting to new challenges and opportunities.
What Does the Future Hold for Google?
The future of Google is closely tied to its ability to innovate and adapt to changing technological landscapes. As a leader in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and cloud computing, Google is well-positioned to capitalize on emerging trends and technologies.
One area of focus is sustainability, with Google committing to operating on carbon-free energy by 2030. This commitment reflects a broader trend in the tech industry towards environmental responsibility and sustainable practices.
Google's future also involves expanding its reach in developing markets, investing in local infrastructure, and adapting its products to meet diverse user needs. By continuing to innovate and prioritize user experience, Google aims to remain a central figure in the digital age.
FAQs
1. Who owns Google?
Google is owned by Alphabet Inc., its parent company. Major shareholders include the company's founders, Larry Page and Sergey Brin, as well as institutional investors like Vanguard Group and BlackRock.
2. What is Alphabet Inc.?
Alphabet Inc. is the parent company of Google, formed in 2015 to manage Google's various business interests and subsidiaries. It allows Google to focus on its core services while overseeing other ventures.
3. How does Google's dual-class share structure work?
Google's dual-class share structure includes Class A shares (GOOGL) and Class B shares with ten times the voting power. This structure allows founders Larry Page and Sergey Brin to maintain control over the company.
4. What are Google's main sources of revenue?
Google's primary revenue source is advertising, but it also earns income from cloud computing, hardware sales, subscriptions, and app services.
5. How does Google's ownership impact its strategy?
The founders' control through Class B shares allows Google to focus on long-term innovation and strategic decisions that align with their vision, while institutional shareholders influence sustainable practices.
6. What are some of Google's environmental initiatives?
Google aims to operate on carbon-free energy by 2030 and invests in sustainable practices and technologies to reduce its environmental impact.
Conclusion
Understanding who owns Google provides valuable insights into the company's strategic direction, governance, and future potential. The unique ownership structure, with its blend of founder control and institutional influence, has been instrumental in shaping Google's success and innovation. As Google continues to evolve and expand, its ownership dynamics will remain a crucial factor in determining its role in the technology landscape and its impact on society.