Ingrown hairs can be more than just a minor inconvenience for many individuals. While often associated with superficial skin irritation, they can sometimes develop into more serious complications. One such complication is when an ingrown hair turns into a hard lump under the skin, causing discomfort and concern. This article delves into the causes, symptoms, prevention, and treatment of ingrown hairs that evolve into hard lumps, providing a comprehensive understanding for those affected.
When dealing with ingrown hairs, it’s essential to recognize the signs early on. While some may resolve on their own, others can lead to painful, hard lumps that might require medical attention. Understanding the progression from a simple ingrown hair to a more severe condition is crucial in managing and preventing these occurrences. By exploring the underlying factors and effective strategies, individuals can take proactive steps to maintain healthy skin and avoid complications.
In this article, we will cover various aspects of ingrown hairs turning into hard lumps under the skin. From identifying symptoms to exploring treatment options, readers will gain valuable insights into managing this common skin issue. With expert advice and practical tips, this guide aims to equip individuals with the knowledge needed to tackle ingrown hair problems head-on and keep their skin healthy and lump-free.
Read also:All About Nikkita Lyons A Rising Star In The World Of Wrestling
Table of Contents
- What are Ingrown Hairs?
- Why Do Ingrown Hairs Occur?
- How Can Ingrown Hairs Turn Into Hard Lumps?
- Symptoms of Ingrown Hair Turned Hard Lump
- Prevention Methods
- Treatment Options for Ingrown Hairs
- When to See a Doctor?
- Home Remedies for Ingrown Hairs
- Professional Treatments
- Lifestyle Changes to Prevent Ingrown Hairs
- Can Ingrown Hairs Lead to Infections?
- Impact of Ingrown Hairs on Skin Health
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What are Ingrown Hairs?
Ingrown hairs occur when a hair grows back into the skin instead of rising up from it. They are common among people who shave, wax, or tweeze to remove unwanted hair. The condition is characterized by small, round bumps called papules, or pus-filled bumps called pustules. Ingrown hairs are often painful and itchy, leading to significant discomfort.
The anatomy of hair growth plays a vital role in understanding ingrown hairs. Hair follicles are small pockets in the skin from which hair grows. When hairs are cut very short or removed completely, they may curl back into the skin, especially if they are naturally curly or coarse. This misdirection causes the hair to grow inward, leading to the formation of ingrown hairs.
Ingrown hairs are not limited to any specific area but are more prevalent in regions subjected to frequent hair removal. This includes the face, neck, legs, and bikini line. While the condition is generally harmless, it can lead to complications if not managed properly, such as infections or the development of hard lumps under the skin.
Why Do Ingrown Hairs Occur?
Several factors contribute to the occurrence of ingrown hairs. The most common cause is hair removal techniques that cut the hair below the skin level. Shaving is the primary culprit, especially when done against the direction of hair growth or with a dull blade. Waxing and tweezing can also lead to ingrown hairs if the hair breaks unevenly or if proper aftercare is not followed.
Genetics also play a significant role in determining susceptibility to ingrown hairs. Individuals with curly or coarse hair are more prone to experiencing ingrown hairs because their hair tends to curl back into the skin more easily. Additionally, certain skin types, particularly those that are thicker or have a higher number of dead skin cells, are more likely to trap hairs beneath the surface.
Improper skincare routines, such as not exfoliating regularly, can exacerbate the problem. Dead skin cells can accumulate on the surface, blocking hair follicles and increasing the likelihood of hairs becoming trapped. Environmental factors, such as humidity and friction from clothing, can further contribute to the development of ingrown hairs.
Read also:May D A Look Into The Life And Career Of The Nigerian Music Sensation
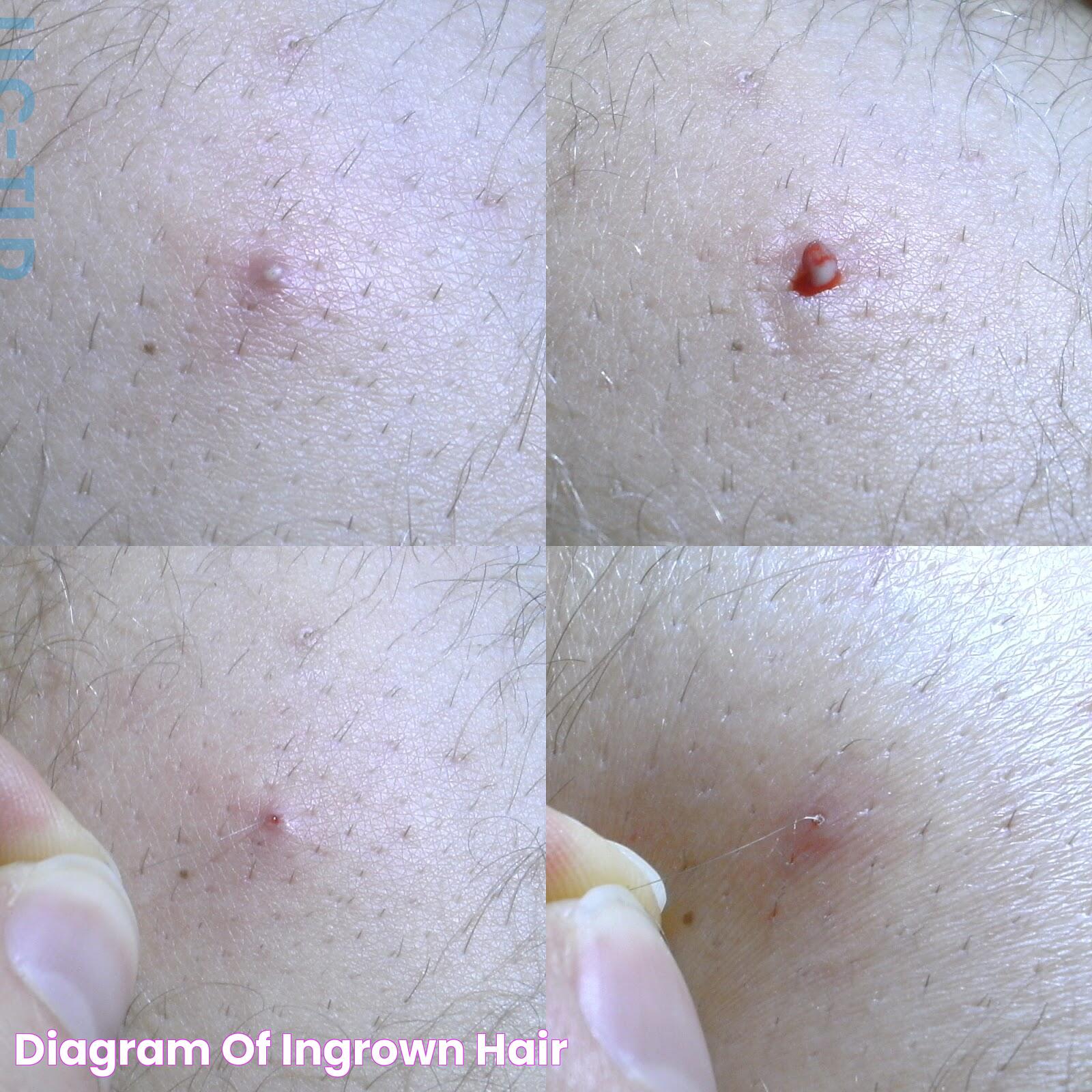
How Can Ingrown Hairs Turn Into Hard Lumps?
Ingrown hairs can sometimes progress from minor irritations to hard lumps under the skin. This occurs when the body mounts an immune response to the ingrown hair, treating it as a foreign object. The area surrounding the hair becomes inflamed, leading to redness, swelling, and eventually, the formation of a hard lump.
The development of a hard lump is often a result of repeated irritation and inflammation. When an ingrown hair is left untreated or is frequently irritated by scratching or tight clothing, it can lead to a condition known as folliculitis. This is an infection of the hair follicle that can cause the lump to become painful and even more pronounced.
In some cases, the lump may become cystic, forming a fluid-filled sac beneath the skin. Cysts can be larger and more painful than simple lumps and may require medical intervention to resolve. It is crucial to address ingrown hairs promptly to prevent them from reaching this stage and causing further complications.
Symptoms of Ingrown Hair Turned Hard Lump
Recognizing the symptoms of an ingrown hair that has turned into a hard lump is essential for timely treatment. Common symptoms include:
- Redness and swelling around the affected area
- Pain or tenderness when touching the lump
- A noticeable bump or lump beneath the skin
- Pus or fluid drainage if an infection is present
- Persistent itching or irritation
These symptoms can vary in intensity depending on the severity of the condition. While some lumps may resolve on their own, others may persist and worsen over time. If left untreated, these lumps can lead to more severe infections or scarring, emphasizing the importance of seeking medical advice if symptoms do not improve.
Prevention Methods
Preventing ingrown hairs from turning into hard lumps involves a combination of proper hair removal techniques and skincare routines. Here are some effective strategies for prevention:
- Use sharp, clean razors and replace them frequently to ensure a close shave without irritation.
- Shave in the direction of hair growth to minimize the risk of hair curling back into the skin.
- Exfoliate regularly to remove dead skin cells and keep hair follicles clear.
- Moisturize the skin to maintain its elasticity and prevent irritation.
- Avoid tight clothing that can cause friction and exacerbate the problem.
By incorporating these practices into daily routines, individuals can significantly reduce the likelihood of developing ingrown hairs and the associated hard lumps. Consistency and attention to detail are key in preventing these skin issues.
Treatment Options for Ingrown Hairs
Treating ingrown hairs, especially those that have turned into hard lumps, requires a multifaceted approach. Depending on the severity of the condition, various treatment options may be considered:
Home Care Strategies
- Warm Compress: Applying a warm compress to the affected area can help soften the skin and allow the hair to emerge naturally.
- Topical Treatments: Over-the-counter creams containing salicylic acid or glycolic acid can help exfoliate the skin and reduce inflammation.
- Gentle Exfoliation: Use a mild exfoliating scrub to remove dead skin cells and help free trapped hairs.
- Avoid Irritation: Refrain from scratching or picking at the lump, as this can worsen the condition.
Medical Interventions
- Antibiotic Creams: If an infection is present, a doctor may prescribe topical antibiotics to clear the infection.
- Incision and Drainage: In severe cases, a healthcare professional may need to make a small incision to drain the cyst.
- Laser Hair Removal: This procedure can permanently reduce hair growth and decrease the risk of ingrown hairs.
Consulting with a dermatologist is advisable for persistent or severe cases to determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
When to See a Doctor?
While many cases of ingrown hairs can be managed at home, certain situations warrant professional medical attention:
- The lump is increasing in size or becoming more painful.
- There is significant redness, warmth, or pus, indicating a possible infection.
- Home treatments have been ineffective in resolving the issue.
- There are signs of spreading infection, such as fever or chills.
Seeking medical advice promptly can prevent complications and ensure appropriate treatment is administered.
Home Remedies for Ingrown Hairs
Several home remedies can help alleviate the discomfort associated with ingrown hairs and promote healing:
- Tea Tree Oil: Known for its antibacterial properties, tea tree oil can reduce inflammation and prevent infection. Dilute it with a carrier oil and apply to the affected area.
- Aloe Vera: The soothing properties of aloe vera can calm irritated skin and promote healing. Apply fresh aloe vera gel directly to the skin.
- Witch Hazel: This natural astringent can help reduce redness and swelling. Dab a small amount onto the lump with a cotton ball.
While these remedies can be effective, it is important to monitor the condition and seek medical advice if symptoms persist.
Professional Treatments
For those who experience recurrent or severe ingrown hairs, professional treatments may offer a long-term solution:
- Laser Hair Removal: This treatment targets hair follicles and reduces hair growth, minimizing the risk of ingrown hairs.
- Electrolysis: A method of permanent hair removal that destroys hair follicles with an electric current.
- Chemical Peels: These can help exfoliate the skin at a deeper level, preventing hair from becoming trapped.
Consulting with a dermatologist can help determine the most suitable treatment based on individual needs and skin type.
Lifestyle Changes to Prevent Ingrown Hairs
In addition to specific treatments, certain lifestyle changes can further reduce the risk of ingrown hairs:
- Improve Skincare Routine: Incorporate regular exfoliation and moisturizing to keep skin healthy.
- Adjust Hair Removal Techniques: Consider switching to methods less likely to cause ingrown hairs, such as using electric razors or depilatory creams.
- Wear Loose Clothing: Reduce friction on the skin by opting for loose-fitting clothes.
By making these adjustments, individuals can maintain smooth, bump-free skin and prevent the recurrence of ingrown hairs.
Can Ingrown Hairs Lead to Infections?
Yes, ingrown hairs can lead to infections, particularly if they are scratched, picked, or left untreated. When a hair becomes trapped beneath the skin, it can cause inflammation and create an environment conducive to bacterial growth. This can result in folliculitis, characterized by pus-filled lesions and increased pain.
Infections from ingrown hairs can spread to surrounding tissues, leading to more significant health concerns if not addressed. It is vital to maintain proper hygiene and avoid irritating the affected area to prevent infections from developing.
Impact of Ingrown Hairs on Skin Health
While ingrown hairs are generally a cosmetic concern, they can have broader implications for skin health if recurrent or severe. Chronic ingrown hairs can lead to:
- Scarring or hyperpigmentation, particularly in individuals with darker skin tones.
- Thickening of the skin due to repeated irritation and inflammation.
- Increased susceptibility to infections and other dermatological conditions.
Addressing ingrown hairs early and adopting preventive measures can help minimize their impact on skin health and maintain a clear complexion.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common causes of ingrown hairs?
Ingrown hairs are commonly caused by improper hair removal techniques, such as shaving against the grain, using dull blades, and not exfoliating regularly. Genetics and certain hair types can also predispose individuals to ingrown hairs.
How can I tell if an ingrown hair has become infected?
Signs of an infected ingrown hair include increased redness, swelling, pus or fluid drainage, and heightened pain or tenderness. If these symptoms occur, it is advisable to seek medical advice.
Are there any long-term solutions for preventing ingrown hairs?
Long-term solutions include professional treatments like laser hair removal or electrolysis, which can reduce or eliminate hair growth and thus prevent ingrown hairs from forming.
Can ingrown hairs cause permanent damage to the skin?
While most ingrown hairs resolve without causing permanent damage, severe or recurrent cases can lead to scarring, hyperpigmentation, or skin thickening. Prompt treatment and preventive measures can help mitigate these risks.
Is it safe to remove an ingrown hair at home?
While it is possible to gently remove an ingrown hair at home using sterilized tools, it is usually safer to allow the hair to emerge naturally or seek professional assistance, especially if the area is inflamed or infected.
What role does exfoliation play in preventing ingrown hairs?
Exfoliation helps remove dead skin cells, preventing them from clogging hair follicles and trapping hairs beneath the skin. Regular exfoliation is an effective preventive measure against ingrown hairs.
Conclusion
Ingrown hairs that develop into hard lumps under the skin can be a source of discomfort and concern. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for managing this common skin issue effectively. Through a combination of proper hair removal techniques, skincare routines, and lifestyle changes, individuals can prevent and address ingrown hairs, maintaining healthy, smooth skin. For persistent or severe cases, seeking professional medical advice ensures appropriate treatment and minimizes the risk of complications, helping individuals achieve a lump-free complexion.